Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
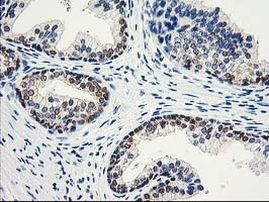
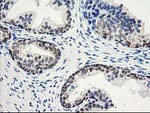
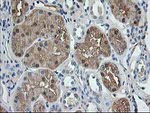
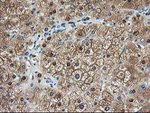
TA503189
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
ACY1 encodes a cytosolic, homodimeric, zinc-binding enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of acylated L-amino acids to L-amino acids and an acyl group, and has been postulated to function in the catabolism and salvage of acylated amino acids. This gene is located on chromosome 3p21. 1, a region reduced to homozygosity in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), and its expression has been reported to be reduced or undetectable in SCLC cell lines and tumors. The amino acid sequence of human aminoacylase-1 is highly homologous to the porcine counterpart, and this enzyme is the first member of a new family of zinc-binding enzymes. Mutations in this gene cause aminoacylase-1 deficiency, a metabolic disorder characterized by central nervous system defects and increased urinary excretion of N-acetylated amino acids. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the upstream ABHD14A (abhydrolase domain containing 14A) gene. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 18.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: ACY-1; acylase; Aminoacylase-1; epididymis secretory protein Li 5; N-acyl-L-amino-acid amidohydrolase
Gene Aliases: 1110014J22Rik; ACY-1; ACY1; ACY1D; HEL-S-5
UniProt ID: (Human) Q03154, (Mouse) Q99JW2
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 95, (Mouse) 109652

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support