Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 1
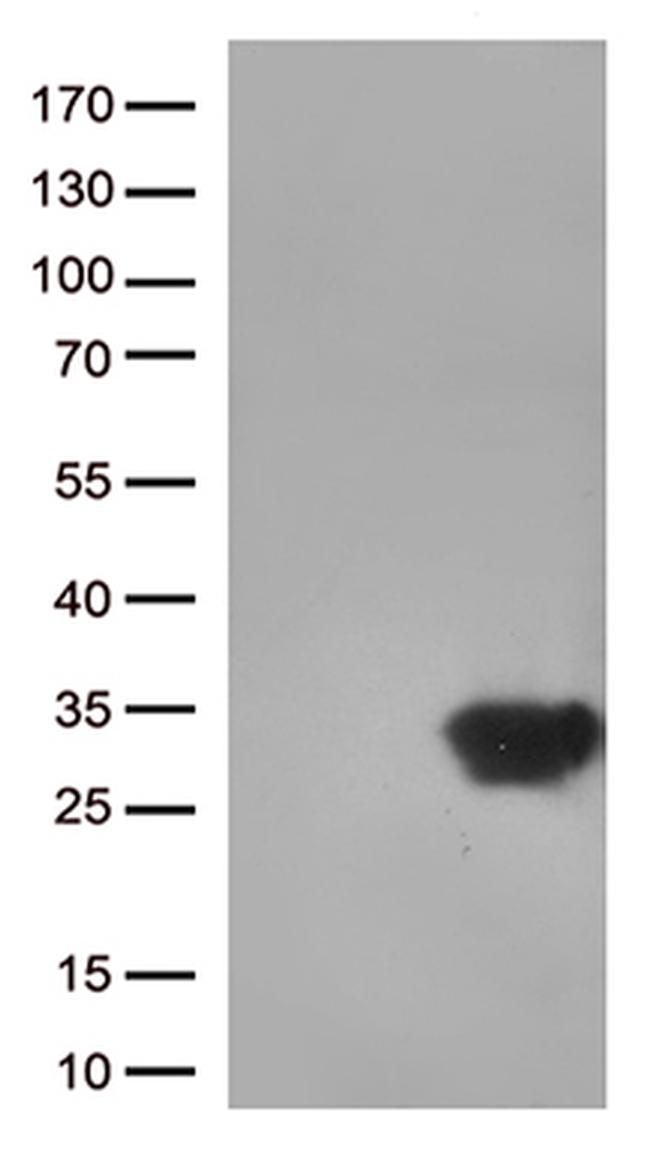
DUSP3 Antibody (TA812964) in WB
Product Details
TA812964
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are a group of enzymes that remove phosphate groups from phosphorylated tyrosine residues on proteins. Together with tyrosine kinases, PTPs regulate the phosphorylation state of many important signaling molecules, such as the MAP kinase family. Recently, increasing attention has been focused on the growing family of PTPs. Like PTKs, PTPs have been implicated in cell signaling, cell growth and proliferation, and oncogenic transformation. Moreover, some PTPs can be involved in cell cycle regulation and embryogenesis. Dual specificity phosphatases (DSPs) are an emerging subclass of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) gene superfamily, which appears to be selective for dephosphorylating the critical phosphothreonine and phosphotyrosine residues. The prototypical DSP is the VH1 gene in vaccinia virus expressed in late-stage viral infection. A shallow active site pocket in VHR allows for the hydrolysis of phosphorylated serine, threonine, or tyrosine protein residues, whereas the deeper active site of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) restricts substrate specificity to only phosphotyrosine.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Dual specificity protein phosphatase 3; Dual specificity protein phosphatase VHR; DUSP 3; DUSP-3; serine/threonine specific protein phosphatase; Vaccinia H1-related phosphatase; vaccinia virus phosphatase VH1-related; VHR
Gene Aliases: DUSP3; VHR
UniProt ID: (Human) P51452
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 1845

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support