Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 3
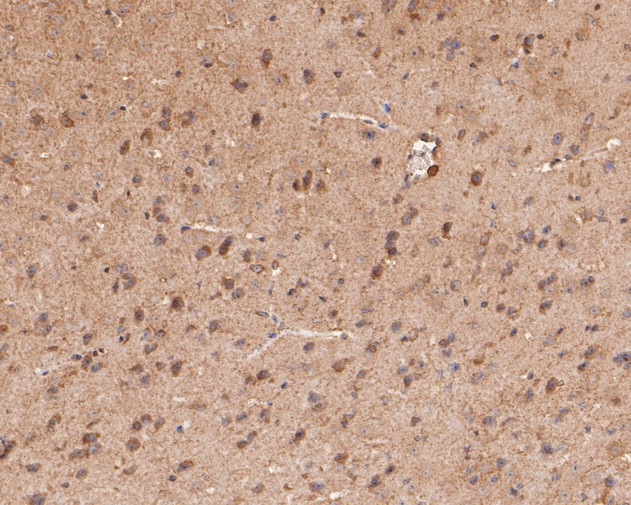
GABRA4 Antibody (PA5-116437) in IHC (P)



Product Details
PA5-116437
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Positive controls: SH-SY5Y cell lysates, rat brain tissue, mouse brain tissue, SH-SY5Y.
Target Information
Gamma-aminobutyric acid is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain where it acts at GABA-A receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABA-A receptor. At least 16 distinct subunits of GABA-A receptors have been identified. This gene encodes subunit alpha-4, which is involved in the etiology of autism and eventually increases autism risk through interaction with another subunit, gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor beta-1. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found in this gene.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: GABA(A) receptor subunit alpha-4; GABA(A) receptor, alpha 4; GABA-A receptor alpha-4 subunit; GABAAR subunit alpha-4; GABAARalpha4; gamma-aminobutyric acid; gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4; gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA-A) receptor, subunit alpha 4; gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor alpha 4; Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-4
Gene Aliases: Gabra-4; GABRA4
UniProt ID: (Human) P48169, (Mouse) Q9D6F4, (Rat) P28471
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 2557, (Mouse) 14397, (Rat) 140675

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support