Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
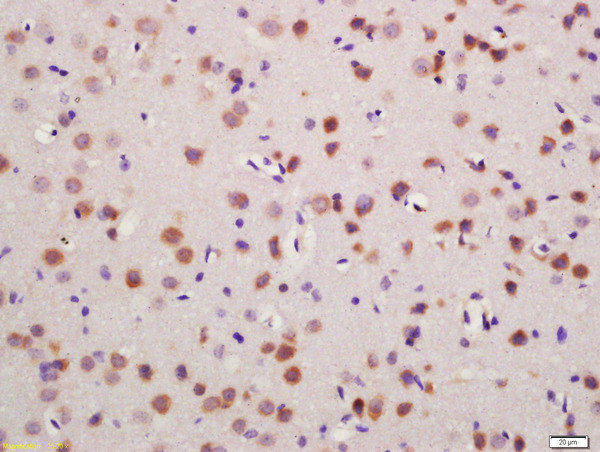
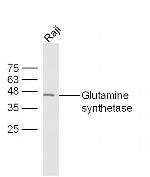
BS-4143R
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Glutamine synthase is part of the glutamine synthetase family. Ammonia incorporation in animals occurs through the actions of glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthase. Glutamate plays the central role in mammalian nitrogen flow, serving as both a nitrogen donor and nitrogen acceptor. It also has an important role in controlling metabolic regulations of neurotransmitter glutamate. Because of the multiple functions and importance of GS in cellular metabolism, both catalytic activities and synthesis are highly regulated. The activity of GS is controlled by adenylylation. Its activity is decreased in the cerebral cortex of brains affected by Alzheimer's disease, particularly in the vicinity of senile plaques. It is also decreased under conditions of glucose deprivation.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: cell proliferation-inducing protein 59; GLNA; Glutamate ammonia ligase; glutamate decarboxylase; Glutamate--ammonia ligase; glutamate-ammonia ligase (glutamine synthase); glutamate-ammonia ligase (glutamine synthetase); glutamine synthase; Glutamine synthetase; Glutamine synthetase (glutamate-ammonia ligase); glutamine synthetase 1; glutamine synthetase I; GS; Palmitoyltransferase GLUL; Proliferation inducing protein 43; proliferation-inducing protein 43
Gene Aliases: GLNS; GLUL; GS; PIG43; PIG59
UniProt ID: (Human) P15104, (Mouse) P15105, (Rat) P09606
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 2752, (Mouse) 14645, (Rat) 24957

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support