Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
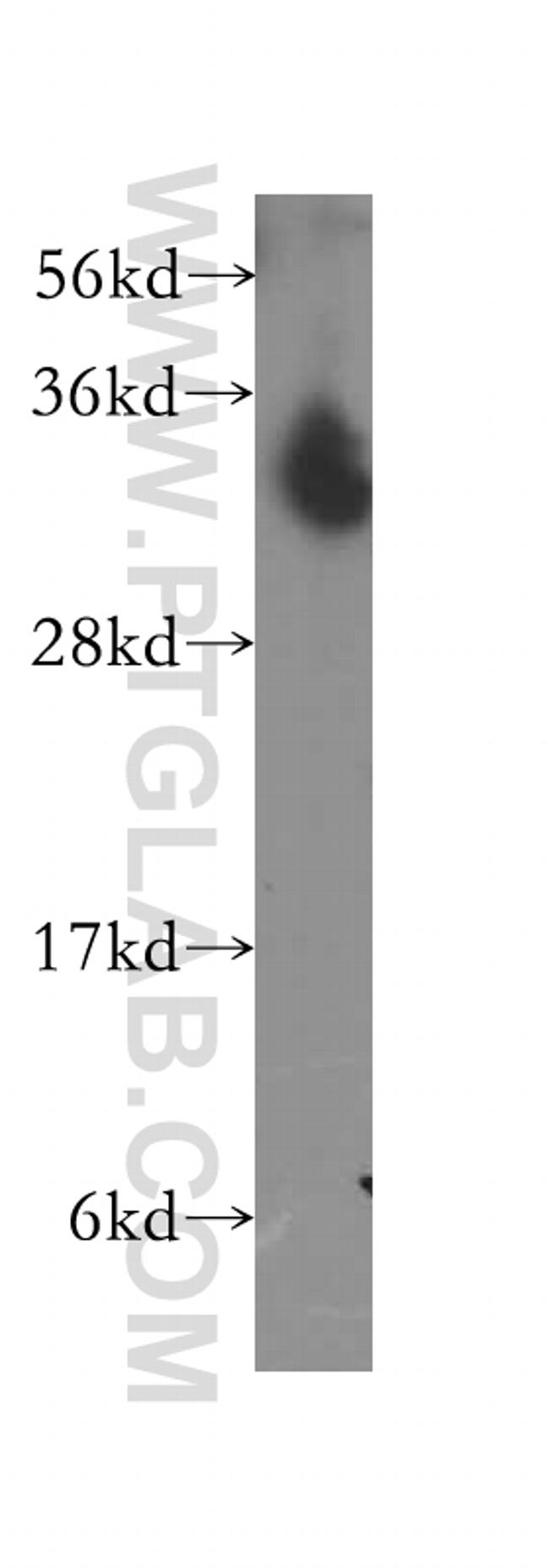
11154-1-AP
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Oxygen radicals damage chromosonal DNA causing cell death and inducing mutations. Although a major focus of oxidatively damaged DNA has centered on the repair of 8-oxo-G, a number of other damaged DNA sites are created by free-radical attack on DNA. The human NTH1 repair protein is one enzyme that has been shown to act on a large number of these other oxidatively damaged DNA sites.A homologue of E. coli Endonuclease III, NTH is a DNA glycosylase with apurinic/apyrimidinic lyase activity. The NTH protein has broad substrate specificity, including numerous ring saturation and fragmentation products of pyrimidines. Research indicates NTH plays a crucial role in removal of oxidative base lesions in mitochondrial DNA.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: bifunctional DNA N-glycoslyase/DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase; Bifunctional DNA N-glycosylase/DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase; DNA glycoslyase/AP lyase; DNA glycosylase/AP lyase; Endonuclease III-like protein 1; hNTH1; nth endonuclease III-like 1; NTHL 1; OCTS 3; thymine glycol DNA glycosylase/AP lyase
Gene Aliases: FAP3; hNTH1; NTH1; NTHL1; OCTS3
UniProt ID: (Human) P78549, (Mouse) O35980
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 4913, (Mouse) 18207, (Rat) 29541

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support