Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 4
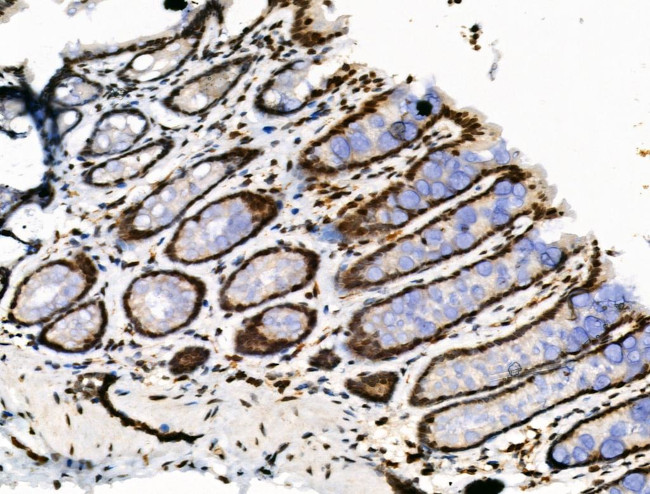
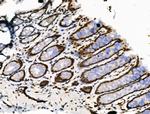
Phospho-DUSP16 (Ser446) Antibody (PA5-106012) in IHC (P)

Product Details
PA5-106012
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
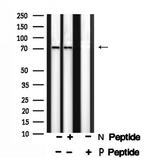
Antibody detects endogenous levels of DUSP16 only when phosphorylated at Ser446.
Target Information
Dual-specificity phosphatases constitute a large heterogeneous subgroup of the type I cysteine-based protein-tyrosine phosphatase superfamily. DUSPs are characterized by their ability to dephosphorylate both tyrosine and serine/threonine residues. DUSP16 belongs to a class of DUSPs, designated MKPs, that dephosphorylate MAPK proteins ERK, JNK, and p38 with specificity distinct from that of individual MKP proteins. MKPs contain a highly conserved C-terminal catalytic domain and an N-terminal Cdc25-like domain. MAPK activation cascades mediate various physiologic processes, including cellular proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and stress responses.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Dual specificity protein phosphatase 16; MAP kinase phosphatase 7; MAP kinase phosphatase-7; map kinase phosphatase-M; MAPK phosphatase-7; MGC129701; MGC129702; Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 7
Gene Aliases: 3830417M17Rik; AW558566; D6Ertd213e; DUSP16; KIAA1700; MKP-7; MKP7; Mkpm
UniProt ID: (Human) Q9BY84
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 80824, (Mouse) 70686, (Rat) 297682

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support