Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
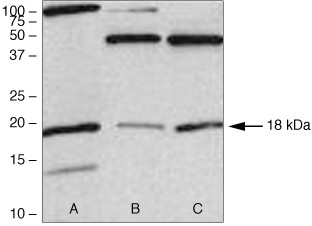
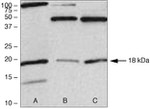
38-3000
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Target Information
The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degradation. Ubiquitination involves at least three classes of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes, or E1s, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2s, and ubiquitin-protein ligases, or E3s. This gene encodes a member of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: mUBC9; OTTHUMP00000198131; p18; RING-type E3 SUMO transferase UBC9; SUMO-1-protein ligase; SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9; SUMO-protein ligase; Ubiquitin carrier protein 9; Ubiquitin carrier protein I; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme 9; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2I; Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 I; ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (homologous to yeast UBC9); ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (UBC9 homolog, yeast); ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcE2A; ubiquitin-like protein SUMO-1 conjugating enzyme; ubiquitin-protein ligase E2I; Ubiquitin-protein ligase I
Gene Aliases: 5830467E05Rik; C358B7.1; F830028O17Rik; P18; UBC9; Ubce2i; UBCE9; UBE2I
UniProt ID: (Human) P63279, (Mouse) P50550
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 7329, (Mouse) 22196

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support