Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Invitrogen
CD209a Monoclonal Antibody (MMD3), Alexa Fluor™ 488, eBioscience™
FIGURE: 1 / 2
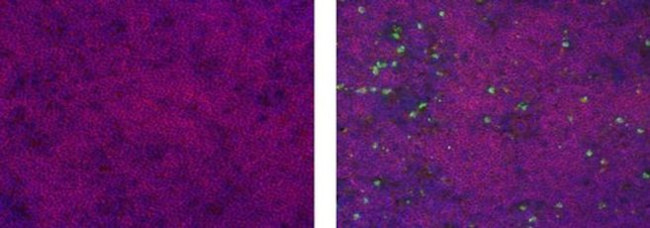
CD209a Antibody (53-2094-82) in IHC (F)


Product Details
53-2094-82
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Conjugate
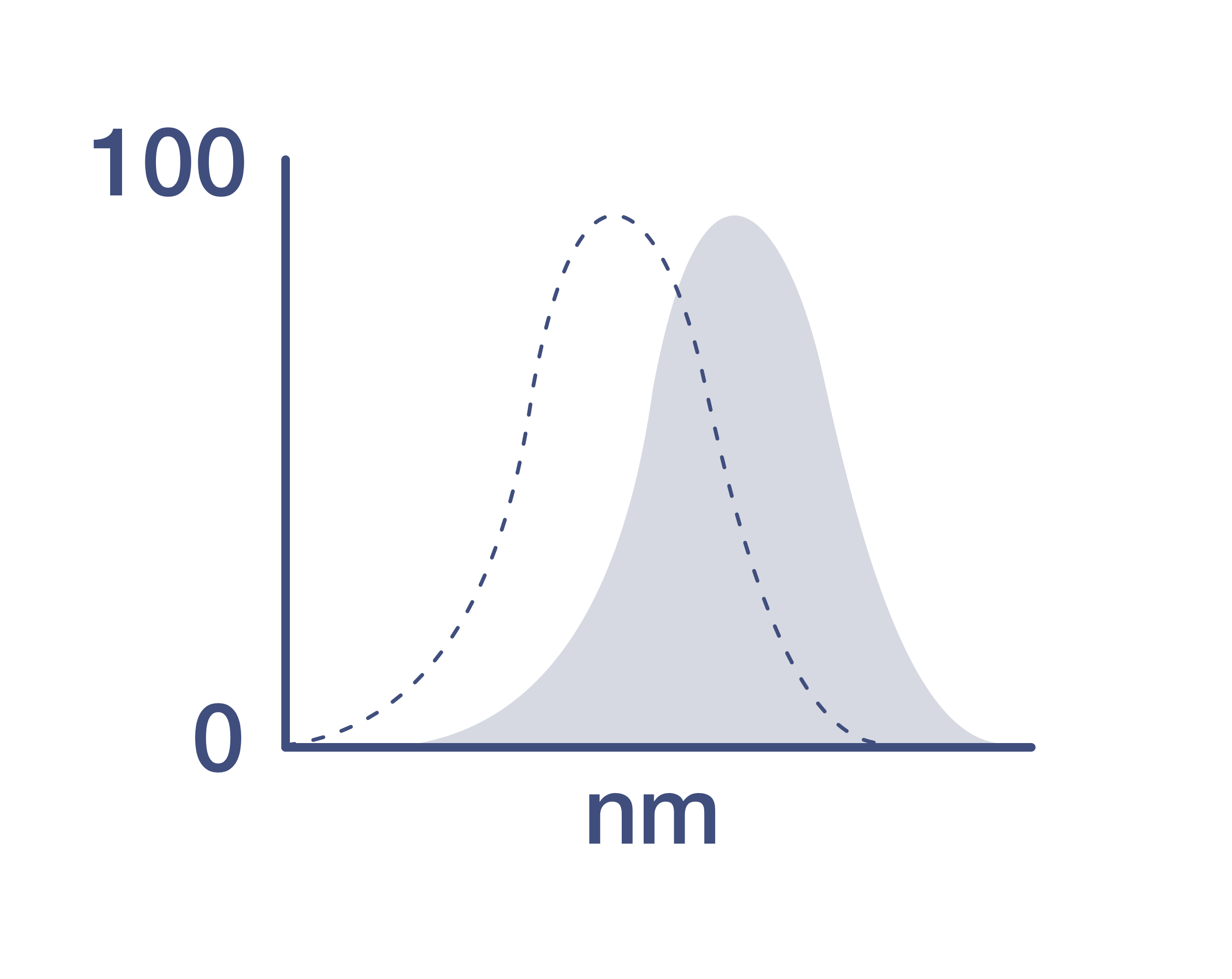
Excitation/Emission Max
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Description: This MMD3 monoclonal antibody recognizes mouse CD209a, which is also known as DC-SIGN. CD209a is a type II transmembrane C-type lectin expressed on a subset of dendritic cells, including some CD4+, CD8- and plasmacytoid pre-dendritic cells. Studies indicate that CD209a expression can vary according to the activation state of the host. Moreover, CD209a is down-regulated in spleen-derived dendritic cell cultures supplemented with GM-CSF. CD209a is involved in mediating the innate immune response by binding microbial carbohydrates.
Cross-blocking studies suggest that MMD3 recognizes a different a different epitope from LWC06 and 5H10.
Applications Reported: This MMD3 antibody has been reported for use in immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections, microscopy, immunohistochemical staining, and immunocytochemistry.
Applications Tested: This MMD3 antibody has been tested by immunohistochemistry on frozen 5-week-old mouse thymus and can be used at less than or equal to 20 µg/mL. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Excitation: 488 nm; Emission: 519 nm; Laser: Blue Laser.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Target Information
This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: CD209; CD209 antigen-like protein A; DC-SIGN; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin; MGC129965; MGC130443
Gene Aliases: CD209; Cd209a; CDSIGN; CIRE; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1; Dcsign; SIGN-R1; SIGNR5
UniProt ID: (Mouse) Q91ZX1
Entrez Gene ID: (Mouse) 170786

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support