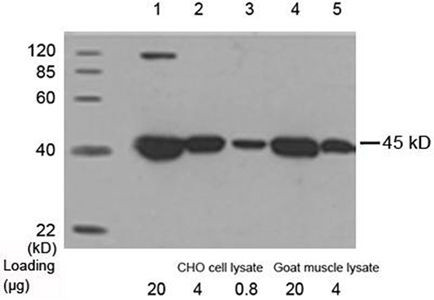
Product References
Negative feedback regulation by HuR controls TRIM21 expression and function in response to UV radiation.
Scientific reports
Guha A,Nag S,Ray PS
Thu Jul 16 00:00:00 EDT 2020
A Novel Role for Necroptosis in the Pathogenesis of Necrotizing Enterocolitis.
Cellular and molecular gastroenterology and hepatology
Werts AD,Fulton WB,Ladd MR,Saad-Eldin A,Chen YX,Kovler ML,Jia H,Banfield EC,Buck RH,Goehring K,Prindle T,Wang S,Zhou Q,Lu P,Yamaguchi Y,Sodhi CP,Hackam DJ
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating disease of premature infants characterized by Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent intestinal inflammation and enterocyte death. Given that necroptosis is a proinflammatory cell death process that is linked to bacterial signaling, we investigated its potential role in NEC, and the mechanisms involved.,Human and mouse NEC intestine were analyzed for necroptosis gene expression (ie, RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL), and protein activation (phosphorylated RI
Mon May 03 00:00:00 EDT 2021
The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ inhibits memory loss, neuropathology, and extends lifespan in aged 3xTg-AD mice.
Molecular and cellular neurosciences
Young ML,Franklin JL
Oxidative stress, likely stemming from dysfunctional mitochondria, occurs before major cognitive deficits and neuropathologies become apparent in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and in mouse models of the disease. We previously reported that treating 2- to 7-month-old 3xTg-AD mice with the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ (mitoquinone mesylate: [10-(4,5-Dimethoxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)decyl](triphenyl)phosphonium methanesulfonate), a period when AD-like pathologies f
Sun Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2019
Relationship between ETS Transcription Factor ETV1 and TGF-β-regulated SMAD Proteins in Prostate Cancer.
Scientific reports
Oh S,Shin S,Song H,Grande JP,Janknecht R
The ETS transcription factor ETV1 is frequently overexpressed in aggressive prostate cancer which is one underlying cause of this disease. Accordingly transgenic mice that prostate-specifically overexpress ETV1 develop prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. However progression to the adenocarcinoma stage is stifled in these mice suggesting that inhibitory pathways possibly preclude ETV1 from exerting its full oncogenic potential. Here we provide evidence that TGF-β/SMAD signaling represents s
Mon Jun 03 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Concomitant type I IFN and M-CSF signaling reprograms monocyte differentiation and drives pro-tumoral arginase production.
EBioMedicine
Tong Y,Zhou L,Yang L,Guo P,Cao Y,Qin FX,Liu J
Type I IFN-based therapies against solid malignancies have yielded only limited success. How IFN affects tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) compartment to impact the therapeutic outcomes are not well understood.
Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2019
Isatin-Schiff base-copper (II) complex induces cell death in p53-positive tumors.
Cell death discovery
Bulatov E,Sayarova R,Mingaleeva R,Miftakhova R,Gomzikova M,Ignatyev Y,Petukhov A,Davidovich P,Rizvanov A,Barlev NA
Medicinal bioinorganic chemistry is a thriving field of drug research for cancer treatment. Transition metal complexes coordinated to essential biological scaffolds represent a highly promising class of compounds for design of novel target-specific therapeutics. We report here the biological evaluation of a novel Isatin-Schiff base derivative and its Cu(II) complex in several tumor cell lines by assessing their effects on cellular metabolism real-time cell proliferation and induction of apoptosi
Wed Oct 04 00:00:00 EDT 2023
Activity of enisamium, an isonicotinic acid derivative, against influenza viruses in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells.
Antiviral chemistry & chemotherapy
Boltz D,Peng X,Muzzio M,Dash P,Thomas PG,Margitich V
New therapeutics for the control of influenza virus infections are needed to alleviate the burden caused by seasonal epidemics and occasional pandemics, and to overcome the potential risk of drug-resistance emergence. Enisamium iodide (Amizon®, Farmak) is currently approved for clinical use for the treatment of influenza in 11 countries which includes Ukraine, Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. However, experimental evidence of the antiviral activity of enisamium has not been repor
Mon Jun 10 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Screening for Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Assembly of Influenza Virus Polymerase Complex by a Bimolecular Luminescence Complementation-Based Reporter System.
Journal of virology
Li C,Wang Z,Cao Y,Wang L,Ji J,Chen Z,Deng T,Jiang T,Cheng G,Qin FX
Influenza virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase consists of three viral protein subunits: PA, PB1 and PB2. Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) of these subunits play pivotal roles in assembling the functional polymerase complex, which is essential for the replication and transcription of influenza virus RNA. Here we developed a highly specific and robust bimolecular luminescence complementation (BiLC) reporter system to facilitate the investigation for influenza virus polymerase complex formation.
Wed Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2017
Integrated STAT3 and Ikaros Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Activities Regulate Bcl-6 Expression in CD4+ Th Cells.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
Read KA,Powell MD,Baker CE,Sreekumar BK,Ringel-Scaia VM,Bachus H,Martin RE,Cooley ID,Allen IC,Ballesteros-Tato A,Oestreich KJ
B cell lymphoma-6 (Bcl-6) is a transcriptional repressor that is required for the differentiation of T follicular helper (TFH) cell populations. Currently, the molecular mechanisms underlying the transcriptional regulation of Bcl-6 expression are unclear. In this study, we have identified the Ikaros zinc finger transcription factors Aiolos and Ikaros as novel regulators of Bcl-6. We found that increased expression of Bcl-6 in CD4+ Th cell populations correlated with enhanced enrichment of Aiolos
Sun Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2017
NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux.
Nature
He Y,Zeng MY,Yang D,Motro B,Núñez G
Inflammasomes are intracellular protein complexes that drive the activation of inflammatory caspases. So far, four inflammasomes involving NLRP1, NLRP3, NLRC4 and AIM2 have been described that recruit the common adaptor protein ASC to activate caspase-1, leading to the secretion of mature IL-1β and IL-18 proteins. The NLRP3 inflammasome has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several acquired inflammatory diseases as well as cryopyrin-associated periodic fever syndromes (CAPS) caused by
Thu Feb 18 00:00:00 EST 2016
Interplay between RNA-binding protein HuR and microRNA-125b regulates p53 mRNA translation in response to genotoxic stress.
RNA biology
Ahuja D,Goyal A,Ray PS
Tumor suppressor protein p53 plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic integrity in response to DNA damage. Regulation of translation of p53 mRNA is a major mode of regulation of p53 expression under genotoxic stress. The AU/U-rich element-binding protein HuR has been shown to bind to p53 mRNA 3'UTR and enhance translation in response to DNA-damaging UVC radiation. On the other hand the microRNA miR-125b is reported to repress p53 expression and stress-induced apoptosis. Here we show that UVC
Tue Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2016
IL-7 signalling represses Bcl-6 and the TFH gene program.
Nature communications
McDonald PW,Read KA,Baker CE,Anderson AE,Powell MD,Ballesteros-Tato A,Oestreich KJ
The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 is linked to the development of both CD4(+) T follicular helper (TFH) and central memory T (TCM) cells. Here, we demonstrate that in response to decreased IL-2 signalling, T helper 1 (TH1) cells upregulate Bcl-6 and co-initiate TFH- and TCM-like gene programs, including expression of the cytokine receptors IL-6Rα and IL-7R. Exposure of this potentially bi-potent cell population to IL-6 favours the TFH gene program, whereas IL-7 signalling represses TFH-a
Fri Jan 08 00:00:00 EST 2016
Trans-presentation of IL-15 modulates STAT5 activation and Bcl-6 expression in TH1 cells.
Scientific reports
Cooley ID,Read KA,Oestreich KJ
During infection naïve CD4(+) T helper cells differentiate into specialized effector subsets based upon environmental signals propagated by the cytokine milieu. Recently this paradigm has been complicated by the demonstration that alterations in the cytokine environment can result in varying degrees of plasticity between effector T helper cell populations. Therefore elucidation of the mechanisms by which cytokines regulate T helper cell differentiation decisions is increasingly important. T
Mon Oct 26 00:00:00 EDT 2015
Basal p21 controls population heterogeneity in cycling and quiescent cell cycle states.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Overton KW,Spencer SL,Noderer WL,Meyer T,Wang CL
Phenotypic heterogeneity within a population of genetically identical cells is emerging as a common theme in multiple biological systems, including human cell biology and cancer. Using live-cell imaging, flow cytometry, and kinetic modeling, we showed that two states-quiescence and cell cycling-can coexist within an isogenic population of human cells and resulted from low basal expression levels of p21, a Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor (CKI). We attribute the p21-dependent heterogeneity
Tue Oct 14 00:00:00 EDT 2014
Fertilization-induced autophagy in mouse embryos is independent of mTORC1.
Biology of reproduction
Yamamoto A,Mizushima N,Tsukamoto S
Autophagy is a dynamically regulated intracellular degradation system that is important for cellular processes such as amino acid production during starvation and intracellular quality control. Previously, we reported that autophagy is suppressed in oocytes but is rapidly up-regulated after fertilization. During this period, autophagy is thought to be important for the generation of amino acids from the bulk degradation of maternal proteins that have accumulated during oogenesis. However, the me
Tue Jul 01 00:00:00 EDT 2014
Optimization of oncogene expression through intra-population competition.
Biotechnology journal
Ferreira JP,Wang CL
Although functional roles have been assigned to many genes - e.g., those involved in cell-cycle regulation, growth signaling, or cancer - considerably less is known about the quantitative relationship between their expression level and outcome. We devised an intra-population competition to study oncogene dosage. Cell populations were engineered to express a range of H-Ras oncogene levels. Cells with different levels of H-Ras then "competed" for an increased share of the total cell popu
Sun Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2013
Oncogenic features of the JMJD2A histone demethylase in breast cancer.
International journal of oncology
Berry WL,Shin S,Lightfoot SA,Janknecht R
Estrogen receptor α (ERα) plays a pivotal role in the genesis of the majority of breast tumors. Consequently, endocrine therapy is now routinely utilized in the clinic for the treatment of ERα-positive breast cancer patients. However, how ERα activity becomes dysregulated in breast cancer cells remains to be elucidated. The aim of this study was to show that the histone demethylase JMJD2A, also known as KDM4A, is capable of forming a complex with ERα in vivo. Moreov
Thu Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2012