Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 2
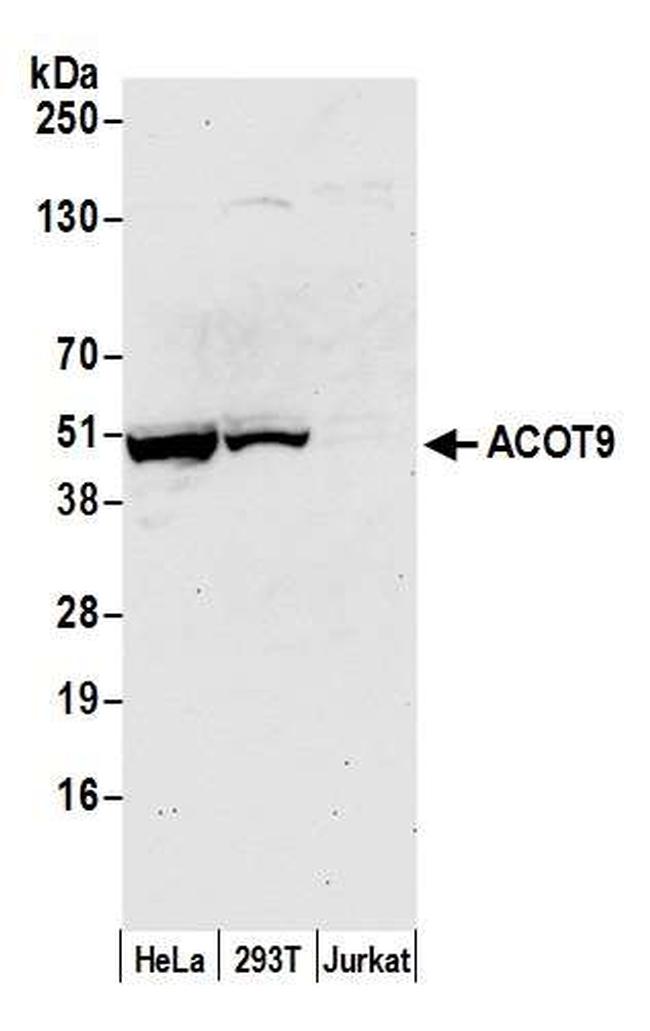
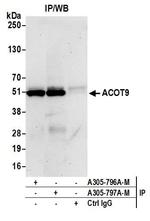
ACOT9 Antibody (A305-797A-T) in WB
Product Details
A305-797A-T
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Acyl-CoA thioesterases (ACOTs) are a group of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of acyl-CoA to form coenzyme A (CoA) and a free fatty acid. Through their catalytic activity, ACOTs are able to regulate the level of fatty acids and acyl-CoAs within the cell. ACOT9 (acyl-CoA thioesterase 9), also known as ACATE2, MT-ACT48 (mitochondrial acyl-CoA thioesterase of 48 kDa) or CGI-16, is a 406 amino acid member of the acyl-CoA hydrolase protein family. ACOT9 contains a C-terminal 80-amino acid domain that is conserved from mouse to human, suggesting that the C-terminus may confer the catalytic activity of ACOT9. The gene encoding ACOT9 is located on chromosome X and the expressed ACOT9 protein is localized to the mitochondrion.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Acyl-CoA thioester hydrolase 9; Acyl-CoA thioesterase 9; acyl-Coenzyme A thioesterase 2, mitochondrial; Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 9, mitochondrial; mitochondrial Acyl-CoA Thioesterase
Gene Aliases: ACATE2; ACOT9; CGI-16; MT-ACT48; MTACT48
UniProt ID: (Human) Q9Y305
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 23597

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support