Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 8
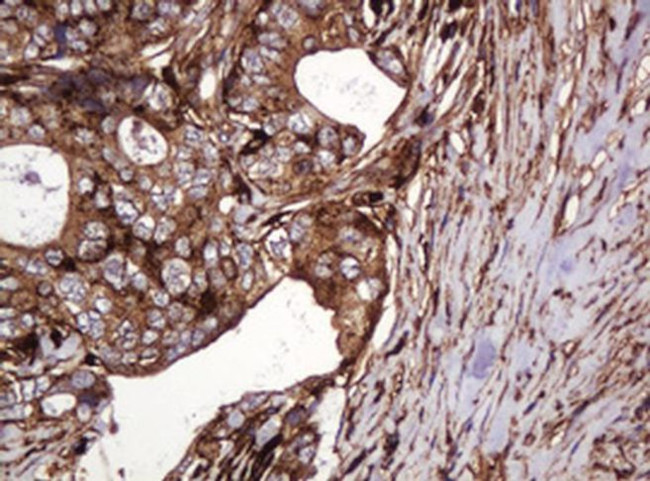
ATP6V1B2 Antibody (MA5-26091) in IHC (P)

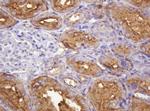
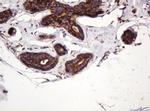
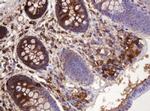
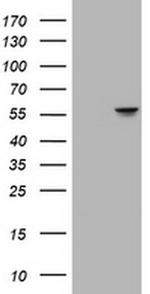
Product Details
MA5-26091
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Target Information
ATP6V1B2 encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A, three B, and two G subunits, as well as a C, D, E, F, and H subunit. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two V1 domain B subunit isoforms and is the only B isoform highly expressed in osteoclasts.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B2; Endomembrane proton pump 58 kDa subunit; H+ transporting two-sector ATPase; HO57; testicular secretory protein Li 65; V-ATPase B2 subunit; V-ATPase subunit B 2; V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform; vacuolar H+-ATPase 56,000 subunit; Vacuolar proton pump subunit B 2
Gene Aliases: ATP6B1B2; ATP6B2; ATP6V1B2; DOOD; HO57; VATB; Vma2; VPP3; ZLS2
UniProt ID: (Human) P21281
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 526

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support