Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
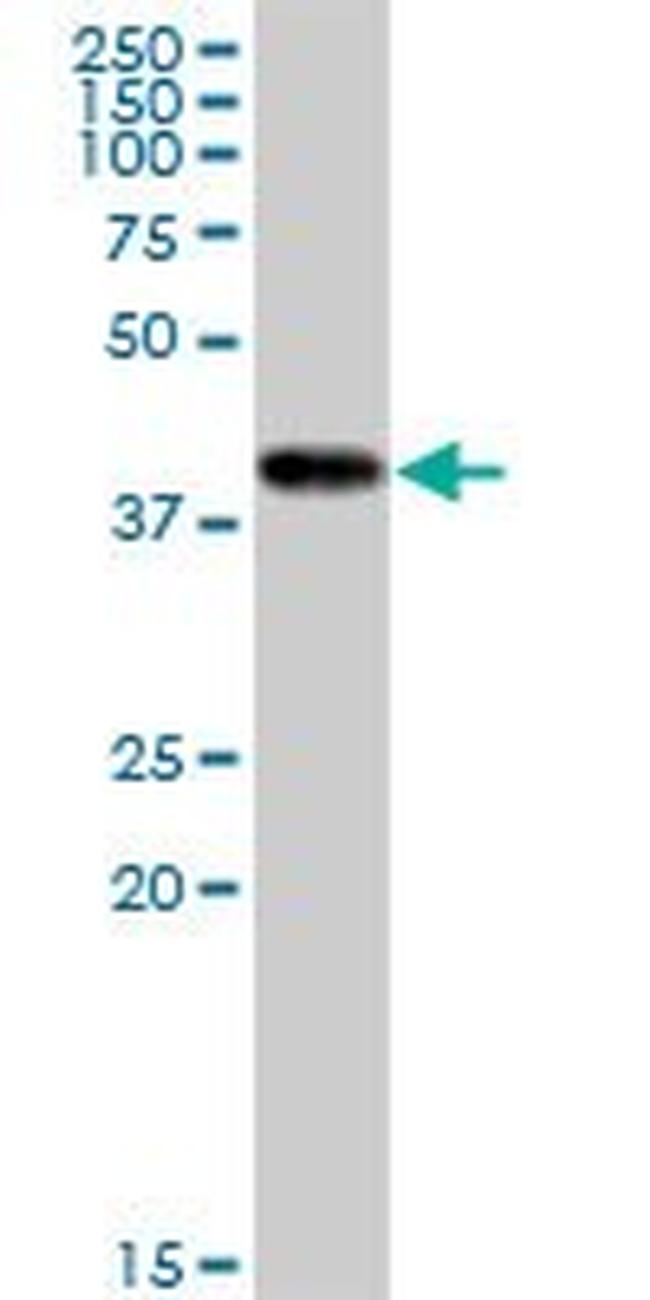
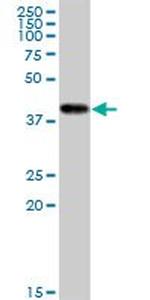
H00001159-M16
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Sequence of this protein is as follows: GVHIKLPLLS KDSRFPKILE NLRLQKRGTG GVDTAATGGV FDISNLDRLG KSEVELVQLV IDGVNYLIDC ERRLERGQDI RIPTPVIHTK H
Target Information
Mitochondrial creatine (MtCK) kinase is responsible for the transfer of high energy phosphate from mitochondria to the cytosolic carrier, creatine. It belongs to the creatine kinase isoenzyme family. It exists as two isoenzymes, sarcomeric MtCK and ubiquitous MtCK, encoded by separate genes. Mitochondrial creatine kinase occurs in two different oligomeric forms: dimers and octamers, in contrast to the exclusively dimeric cytosolic creatine kinase isoenzymes. Many malignant cancers with poor prognosis have shown overexpression of ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase; this may be related to high energy turnover and failure to eliminate cancer cells via apoptosis. Ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase has 80% homology with the coding exons of sarcomeric mitochondrial creatine kinase. Two genes located near each other on chromosome 15 have been identified which encode identical mitochondrial creatine kinase proteins.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Acidic-type mitochondrial creatine kinase; Creatine kinase U-type, mitochondrial; creatine kinase, mitochondrial 1 (ubiquitous); Mia-CK; U-MtCK; Ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase
Gene Aliases: CKMT; CKMT1; CKMT1A; CKMT1B; UMTCK
UniProt ID: (Human) P12532
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 1159

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support