Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 3
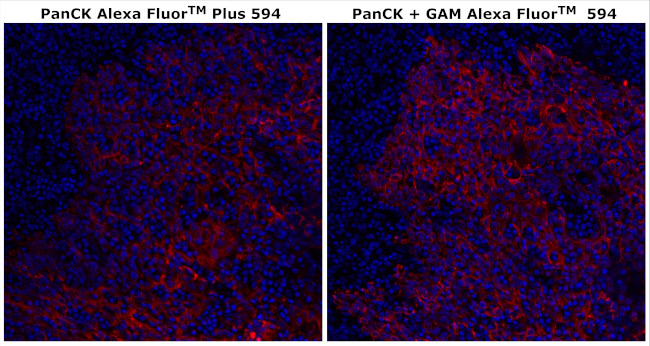
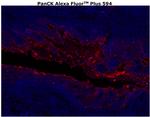
Cytokeratin Pan Type I/II Antibody (755-9003-82) in IHC (P)
Product Details
755-9003-82
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
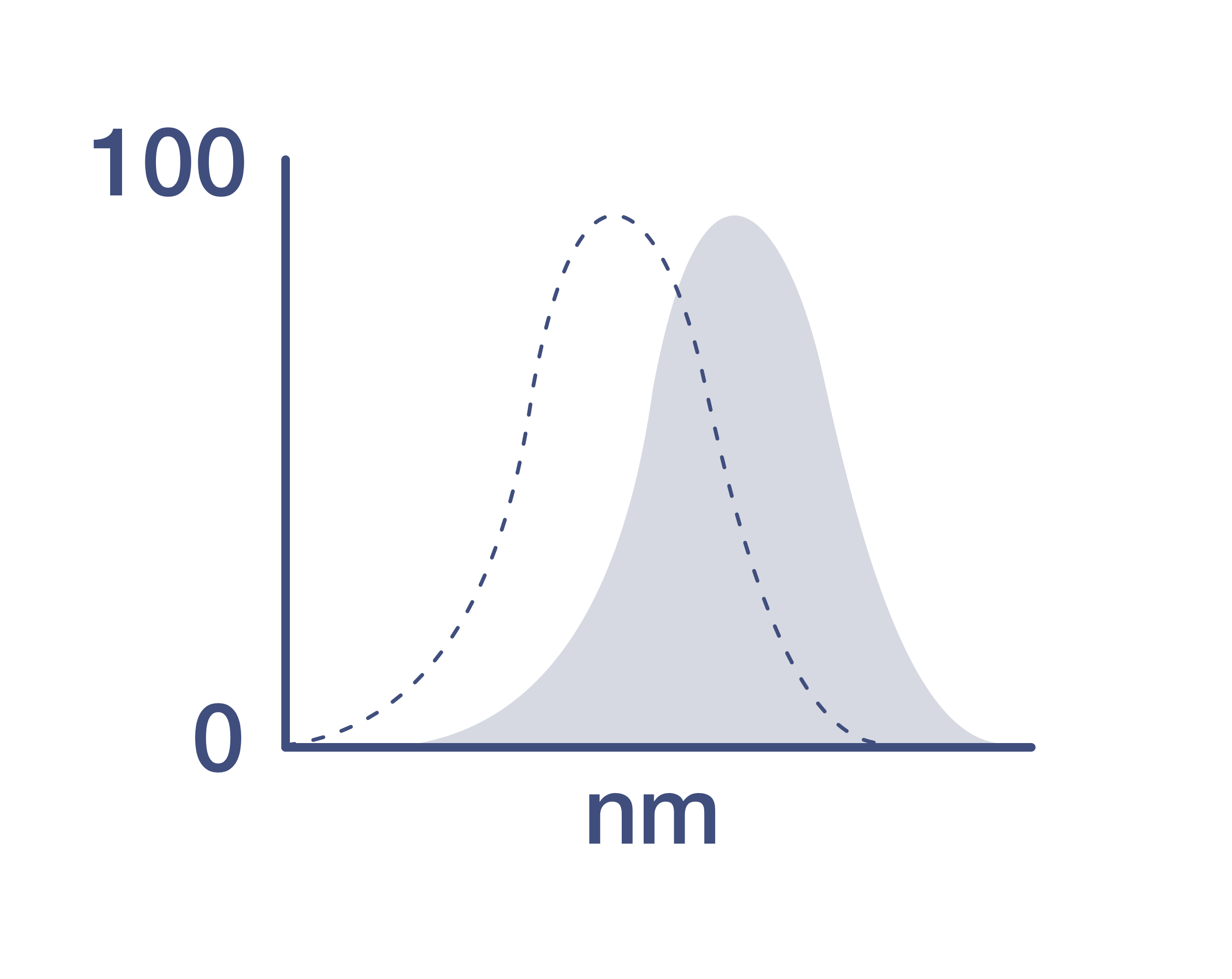
Excitation/Emission Max
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Description: The monoclonal antibodies AE1 and AE3 recognize many of the acidic and basic cytokeratin family members. Cytokeratins are intermediate filament proteins comprising one component of the cytoskeleton. There are two large families of cytokeratins, acidic and basic, but all contain the same basic domains (i.e. an alpha-helical core with an N- and C-terminal domain). The proteins are expressed in epithelial cells, but are developmentally regulated. Many tumors also express these proteins and their expression can help identify the origin of a neoplasm.
The AE3 monoclonal antibody recognizes the 65 to 67 triplet, 64, 59, 58, 56, 54 and 52kD proteins also known as cytokeratin 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 while the AE1 antibody recognizes 56.5, 54', 50, 50', 48, and 40 kDa proteins (also known as CK10, 14, 15, 16 and 19). These antibodies can be used on a wide array of tissue samples from mouse, human, rat, primates (cynomolgus and rhesus), dog, cat, rabbit, and chicken.
Applications Reported: This AE1/AE3 antibody has been reported for use in immunohistochemical staining, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections, and immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue sections.
Applications Tested: This AE1/AE3 antibody has been tested by immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue using high pH antigen retrieval conditions and can be used at 4 µg/mL. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Using conjugate solutions: Centrifuge the protein conjugate solution briefly in a microcentrifuge before use; add only the supernatant to the experiment. This step will help eliminate any protein aggregates that may have formed during storage, thereby reducing nonspecific background staining.
Target Information
Cytokeratin pan is part of a subfamily of intermediate filament proteins that are characterized by remarkable biochemical diversity, and represented in human epithelial tissues by at least 20 different polypeptides. Cytokeratins range in molecular weight between 40 kDa- 68 kDa, and an isoelectric pH between 4.9-7.8. The individual human cytokeratins are numbered 1 to 20. The various epithelia in the human body usually express cytokeratins which are not only characteristic of the type of epithelium, but also related to the degree of maturation or differentiation within an epithelium. Cytokeratin subtype expression patterns are used to an increasing extent in the distinction of different types of epithelial malignancies. The cytokeratin antibodies are not only of assistance in the differential diagnosis of tumors using immunohistochemistry on tissue sections, but are also a useful tool in cytopathology and flow cytometric assays. The composition of cytokeratin pairs vary with the epithelial cell type, stage of differentiation, cellular growth environment, and disease state. Many studies have shown the usefulness of keratins as markers in cancer research and tumor diagnosis.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: 39.1; 40-kDa keratin intermediate filament; 58 kDa cytokeratin; 65 kDa cytokeratin; 67 kDa cytokeratin; Cell proliferation-inducing gene 46 protein; CK-1; CK-10; CK-13; CK-14; CK-15; CK-16; CK-17; CK-18; CK-19; CK-1B; CK-2e; CK-2P; CK-3; CK-4; CK-5; CK-6A; CK-6D; CK-7; CK-8; cytokeratin 1; cytokeratin 10; cytokeratin 13; cytokeratin 14; cytokeratin 15; cytokeratin 16; cytokeratin 18; cytokeratin 19; cytokeratin 2; cytokeratin 3; cytokeratin 4; cytokeratin 6A; cytokeratin 6C; cytokeratin 6D; cytokeratin 7; Cytokeratin-1; Cytokeratin-10; Cytokeratin-13; Cytokeratin-14; Cytokeratin-15; Cytokeratin-16; Cytokeratin-17; Cytokeratin-18; Cytokeratin-19; Cytokeratin-1B; Cytokeratin-2e; Cytokeratin-2P; Cytokeratin-3; Cytokeratin-4; Cytokeratin-5; Cytokeratin-6A; cytokeratin-6C; Cytokeratin-6D; cytokeratin-6E; Cytokeratin-7; Cytokeratin-8; epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2 Dowling-Meara/Kobner/Weber-Cockayne types; epidermolytic hyperkeratosis 1; Epithelial keratin-2e; focal non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma; Hair alpha protein; HMWCK; K1; K10; K13; K14; K15; K16; K17; K18; K19; K1B; K2e; K2P; K3; K4; K5; K6A; K7; K76; K77; K8; kamp-keratin derived antimicrobial peptide; KDAMP; keratin 1, type II; keratin 10, type I; keratin 13, type I; keratin 14, type I; keratin 15, type I; keratin 16, type I; keratin 17, type I; keratin 18, type I; keratin 19, type I; Keratin 1B; keratin 2, type II; keratin 2p; keratin 3, type II; keratin 4, type II; keratin 5 (epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling-Meara/Kobner/Weber-Cockayne types); keratin 5, type II; keratin 6A, , type II; keratin 6A, type II; keratin 7, type II; keratin 76, type II; keratin 77, type II; keratin 8, type II; keratin K6h; Keratin type II cytoskeletal 5; keratin, 55K type II cytoskeletal; keratin, epidermal type II, K6A; keratin, simple epithelial type I, K7; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 18; Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19; keratin, type I, 40-kd; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1b; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 oral; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 3; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7; Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8; Keratin-1; Keratin-10; Keratin-13; Keratin-14; Keratin-15; keratin-15, basic; keratin-15, beta; Keratin-16; Keratin-17; Keratin-18; Keratin-19; Keratin-2 epidermis; Keratin-2e; Keratin-3; Keratin-4; Keratin-5; Keratin-6A; keratin-6C; Keratin-7; Keratin-76; Keratin-77; Keratin-8; KRT1B; pan Cytokeratin; pan keratin; pankeratin; Sarcolectin; type I cytoskeletal 15; type II cytoskeletal 1b; type II mesothelial keratin K7; Type-II keratin Kb1; type-II keratin Kb12; Type-II keratin Kb2; Type-II keratin Kb3; Type-II Keratin Kb39; Type-II keratin Kb4; Type-II keratin Kb5; Type-II keratin Kb6; Type-II keratin Kb7; Type-II keratin Kb8; Type-II keratin Kb9
Gene Aliases: 39.1; BCIE; BIE; CARD2; CK-17; CK-18; CK-2e; CK-4; CK-6C; CK-6E; CK-8; CK1; CK10; CK13; CK14; CK15; CK16; CK19; CK3; CK4; CK5; CK6A; CK6C; CK6D; CK7; CK8; CYK18; CYK4; CYK8; DDD; DDD1; EBS2; EBS3; EBS4; EHK; EHK1; EPPK; FNEPPK; HUMCYT2A; K1; K10; K13; K14; K15; K16; K17; K18; K19; K1B; K1CO; K1CP; K1CS; K2C7; K2C8; K2e; K3; K4; K5; K6A; K6C; K6D; K7; K8; KO; KPP; KRT1; KRT10; KRT13; KRT14; KRT15; KRT16; KRT16A; KRT17; KRT18; KRT19; KRT1A; KRT1B; KRT2; KRT2A; KRT2B; KRT2E; KRT2P; KRT3; KRT4; KRT5; KRT5A; KRT6A; KRT6C; KRT6D; KRT7; KRT76; KRT77; KRT8; KRTA; KRTB; KRTE; NEPPK; NFJ; PC; PC1; PC2; PC3; PCHC1; PIG46; SCL; WSN1; WSN2

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support