Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 2
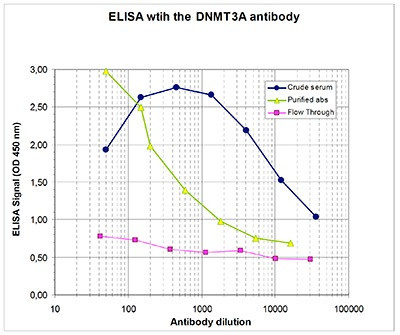
DNMT3A Antibody (BS-53128R) in ELISA


Product Details
BS-53128R
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Methylation of DNA at cytosine residues plays an important role in regulation of gene expression, genomic imprinting and is essential for mammalian development. Hypermethylation of CpG islands in tumor suppressor genes or hypomethylation of bulk genomic DNA may be linked with development of cancer. To date, 3 families of mammalian DNA methyltransferase genes have been identified which include Dnmt1, Dnmt2 and Dnmt3. Dnmt1 is constitutively expressed in proliferating cells and inactivation of this gene causes global demethylation of genomic DNA and embryonic lethality. Dnmt2 is expressed at low levels in adult tissues and its inactivation does not affect DNA methylation or maintenance of methylation. The Dnmt3 family members, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b, are strongly expressed in ES cells but their expression is down regulated in differentiating ES cells and is low in adult somatic tissue. Recently, it has been shown that naturally occurring mutations of Dnmt3b gene occurs in patients with a rare autosomal recessive disorder, termed ICF (immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, and facial anomalies) syndrome.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: AU015806; Cysteine methyltransferase DNMT3A; DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A; DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha; DNA cytosine methyltransferase 3A2; DNA methyltransferase HsaIIIA; DNA MTase HsaIIIA; Dnmt3a; W91664
Gene Aliases: DNMT3A; DNMT3A2; M.HsaIIIA; TBRS
UniProt ID: (Human) Q9Y6K1
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 1788

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support