Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
NeoBiotechnologies
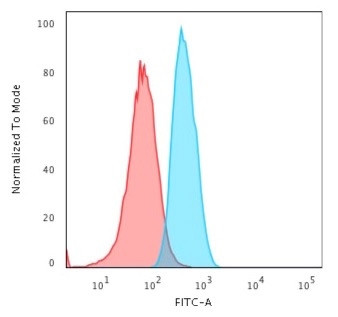
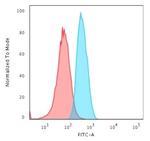
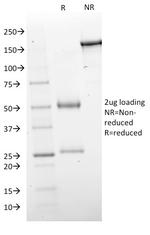
GAD1/GAD67 (GABAergic Neuronal Marker) Monoclonal Antibody (GAD1/2563)
Product Details
2571-MSM3-P1ABX
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
GAD-65 and GAD-67 are members of the group II decarboxylase family of proteins and are responsible for catalyzing the rate limiting step in the production of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) from L-glutamic acid. Although both GADs are found in the brain, GAD-65 localizes to synaptic vesicle membranes in nerve terminals, while GAD-67 is distributed throughout the cell. GAD-67 is responsible for the basal levels of GABA synthesis. In the case of a heightened demand for GABA in neurotransmission, GAD-65 will transiently activate to assist in GABA production. The loss of GAD-65 is detrimental and can impair GABA neurotransmission, however the loss of GAD-67 is lethal. Due to alternative splicing, two isoforms exist for GAD-67: the predominant GAD-67 form and the minor GAD-25 form.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: 67 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase; FLJ45882; GAD 67; GAD-67; Glutamate decarboxylase 1; glutamate decarboxylase 1 (brain, 67kDa); Glutamate decarboxylase 67 kDa isoform; OTTHUMP00000041055
Gene Aliases: CPSQ1; GAD; GAD1; GAD67; SCP
UniProt ID: (Human) Q99259
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 2571

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support