Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
H00002770-M01
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
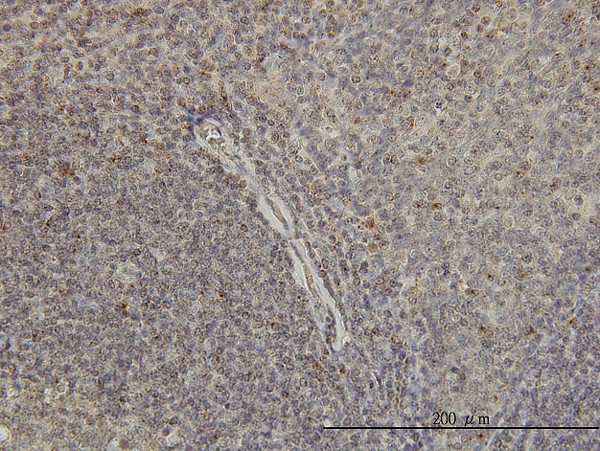
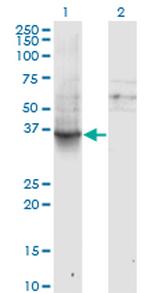
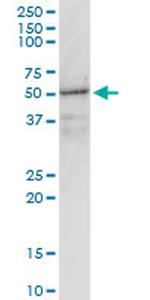
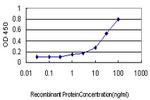
Product Specific Information
Sequence of this protein is as follows: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID RNLREDGEKA AREVKLLLLG AGESGKSTIV KQMKIIHEAG YSEEECKQYK AVVYSNTIQS IIAIIRAMGR LKIDFGDSAR ADDARQLFVL AGAAEEGFMT AELAGVIKRL WKDSGVQACF NRSREYQLND SAAYYLNDLD RIAQPNYIPT QQDVLRTRVK TTGIVETHFT FKDLHFKMFD VGGQRSERKK WIHCFEGVAA IIFCVALSDY DLVLAEDEEM NRMHESMKLF DSICNNKWFT DTSIILFLNK KDLFEEKIKK SPLTICYQEY AGSNTYEEAA AYIQCQFEDL NKRKDTKEIY THFTCATDTK NVQFVFDAVT DVIIKNNLKD CGLF
Target Information
Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) form a large family of signal-transducing molecules. They are found as heterotrimers made up of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. Members of the G protein family have been characterized most extensively on the basis of the alpha subunit, which binds guanine nucleotide, is capable of hydrolyzing GTP, and interacts with specific receptor and effector molecules. The G protein family includes Gs and Gi, the stimulatory and inhibitory GTP-binding regulators of adenylate cyclase; Go, a protein abundant in brain; and transducin-1 and transducin-2, proteins involved in phototransduction in retinal rods and cones, respectively.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G alpha protein; Gi1 protein alpha subunit; guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1; Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1
Gene Aliases: Gi; GNAI1
UniProt ID: (Human) P63096
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 2770

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support