Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
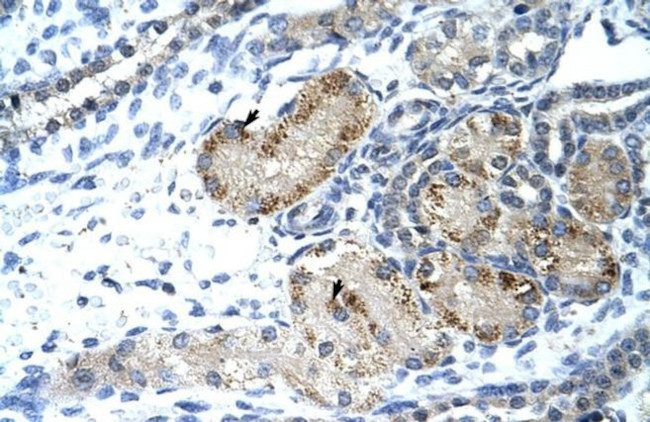
PA5-40769
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Peptide sequence: TFGSQNLERI LAVADKIKFT VTRPFQGLIP KPDEDDANRL GEKVILREQV
Sequence homology: Cow: 100%; Dog: 100%; Guinea Pig: 100%; Horse: 100%; Human: 100%; Mouse: 100%; Rabbit: 100%; Rat: 100%
Target Information
Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS) is a developmental disorder caused by the hemizygous microdeletion on chromosome 7q11.23. WBS is an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is characterized by physical, cognitive and behavioral traits. The physical traits associated with WBS include facial dysmorphology, vascular stenoses, growth deficiencies, dental anomalies and neurologic and musculoskeletal abnormalities. Mild retardation, a weakness in visual-spatial skills, anxiety and a short attention span are typical cognitive and behavioral traits of WBS patients. The WBSCR11 gene is located within the WBS deletion and may contribute to the developmental symptoms found in WBS because of a loss of the encoded transcription factor. WBSCR11 is also designated GRF2IRD1, GTF3, Cream1 and MusTRD1 in human and BEN in mouse, due to slight differences in gene structure. WBSCR11 is expressed in all adult tissues as several variants and has discrete spatial and temporal expression during embryogenesis.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: binding factor for early enhancer; general transcription factor 3; General transcription factor II-I repeat domain-containing protein 1; General transcription factor III; GTF2I repeat domain-containing protein 1; Muscle TFII-I repeat domain-containing protein 1; muscle TFII-I repeat domain-containing protein 1 alpha 1; MusTRD1/BEN; Slow-muscle-fiber enhancer-binding protein; USE B1-binding protein; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 11 protein; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 12 protein; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosome region 11
Gene Aliases: BEN; CREAM1; GTF2IRD1; GTF3; hMusTRD1alpha1; MUSTRD1; RBAP2; WBS; WBSCR11; WBSCR12
UniProt ID: (Human) Q9UHL9
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 9569

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support