Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 1
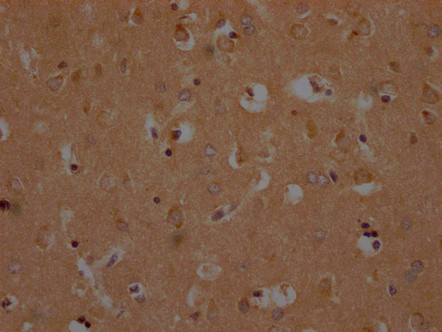
OR10A2 Antibody (PA5-144365) in IHC (P)
Product Details
PA5-144365
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Target Information
Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell. The olfactory receptor proteins are members of a large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) arising from single coding-exon genes. Olfactory receptors share a 7-transmembrane domain structure with many neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and are responsible for the recognition and G protein-mediated transduction of odorant signals. The olfactory receptor gene family is the largest in the genome. The nomenclature assigned to the olfactory receptor genes and proteins for this organism is independent of other organisms.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: HP4; hP4 olfactory receptor; Olfactory receptor 10A2; olfactory receptor OR11-82 pseudogene; Olfactory receptor OR11-86; olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily A, member 2 pseudogene
Gene Aliases: OR10A2; OR10A2P; OR11-82; OR11-86; OST363
UniProt ID: (Human) B2RNL9
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 341276

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support