Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Invitrogen
Phospho-IkB alpha (Ser32, Ser36) Monoclonal Antibody (RILYB3R), PE, eBioscience™
FIGURE: 1 / 2
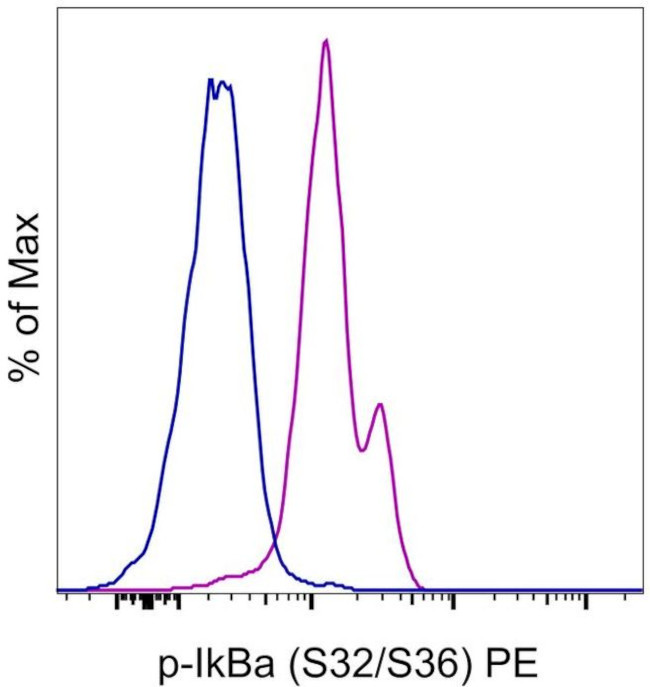
Phospho-IkB alpha (Ser32, Ser36) Antibody (12-9035-42) in Flow
Product Details
12-9035-42
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Recommended Isotype Control
Class
Type
Clone
Conjugate
Excitation/Emission Max
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Description: This RILYB3R monoclonal antibody recognizes human and mouse nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor, alpha (I kappa B alpha) when phosphorylated on serines 32 and 36 (S32/S36). I kappa B alpha is one member of a family of cellular proteins that functions to inhibit classical/canonical NF-kappa B signaling by masking the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-kappa B proteins and keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the cytoplasm. Classical/canonical NF-kappa B signaling is initiated in response to myriad stimuli including engagement of T cell and B cell receptors, growth factors, and inflammatory stimuli (reactive oxygen species, TNF alpha, IL-1) and results in the activation of the I kappa B kinase (IKK) complex that includes IKK alpha, IKK beta, and NEMO. IKK phosphorylates I kappa B alpha resulting in its ubiquitination, degradation, and subsequent translocation of NF-kappa B transcription factor proteins into the nucleus.
Applications Reported: This RILYB3R antibody has been reported for use in intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis.
Applications Tested: This RILYB3R antibody has been pre-titrated and tested by intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis of normal human peripheral blood cells. This can be used at 5 µL (0.125 µg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Staining Protocol: Protocol A and Protocol C are recommended for this monoclonal antibody. Use of Protocol A: Two-step protocol: intracellular (cytoplasmic) proteins allows for the greatest flexibility for detection of surface and intracellular (cytoplasmic) proteins. Protocol C: Two-step protocol: Fixation/Methanol allows for the greatest discrimination of phospho-specific signaling between unstimulated and stimulated samples, but with limitations on the ability to stain specific surface proteins (refer to "Clone Performance Following Fixation/Permeabilization" located in the Best Protocols Section under the Resources tab online). All Protocols can be found in the Flow Cytometry Protocols: "Staining Intracellular Antigens for Flow Cytometry Protocol" located in the Best Protocols Section under the Resources tab online.
Emission: 578 nm; Laser: Blue Laser, Green Laser, Yellow-Green Laser.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Target Information
IkB-alpha is a 40 kDa protein that functions to inhibit NF- kappaB activity. The inhibition occurs via protein-protein interaction between I kappaB proteins and NF- kappaB dimers in the cytosol. The interaction of I kappa B-alpha with NF- kappaB masks the nuclear localization sequence of NF- kappaB, preventing NF- kappaB translocation to the nucleus. A variety of stimuli can activate gene expression by liberating NF- kappaB through the degradation of I kappaB alpha. These stimuli include the proinflammatory cytokines TNF- alpha and IL-1 beta, chemokines, PMA, growth factors, LPS, UV irradiation, viral infection, as well as various chemical and physical stresses. In humans, the gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 14. Activation of NFkB requires that IkB be phosphorylated on specific serine residues, which results in targeted degradation of IkB. IkB kinase alpha (IKK alpha), previously designated CHUK, interacts with IkB-alpha and specifically phosphorylates IkB-alpha on the sites that trigger its degradation Serines 32 and 36. IKK alpha appears to be critical for NFkB activation in response to proinflammatory cytokines. Phosphorylation of IkB by IKK alpha is stimulated by the NFkB inducing kinase (NIK), which itself is a central regulator for NFkB activation in response to TNF and IL-1. The functional IKK complex contains three subunits, IKK alpha, IKK beta and IKK gamma, and each appear to make essential contributions to IkB phosphorylation.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
How to use the Panel Builder
Watch the video to learn how to use the Invitrogen Flow Cytometry Panel Builder to build your next flow cytometry panel in 5 easy steps.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: I(Kappa)B(alpha); I-kappa-B-alpha; I-kappaBalpha; IkappaBalpha; IkB-alpha; IKBalpha; Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha; nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells; nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; nuclear factor of kappa light polyp gene enhancer in B-cell 1; nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha
Gene Aliases: AI462015; IKBA; MAD-3; MAD3; NFKBI; NFKBIA
UniProt ID: (Human) P25963, (Mouse) Q9Z1E3
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 4792, (Mouse) 18035

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support