Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
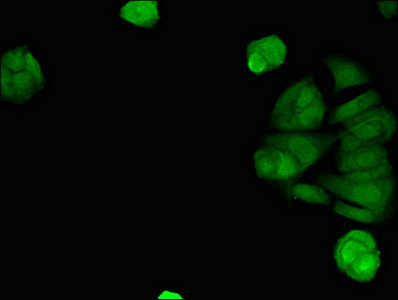
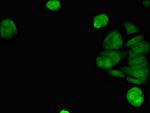
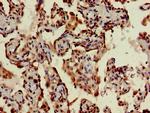
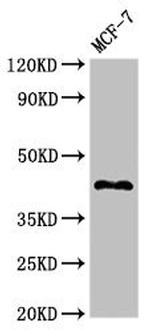
PA5-112749
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Target Information
STING is a 379 amino acid containing signaling protein that acts as an important component of innate immune signaling. This signaling protein is able to activate both NF-kappa-B and IRF3 transcription pathways to induce expression of type I interferon (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and exert a potent anti-viral state following expression. STING may have translocon function, the translocon possibly being able to influence the induction of type I interferons and is also involved in transduction of apoptotic signals via its association with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) thus facilitating the detection of intracellular viral RNA species as well as B-form DNA and mediates death signaling via activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Generally seen in endoplasmic reticulum membrane, cell membrane and mitochondrion outer membrane, it is ubiquitously expressed in most of tissues.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: endoplasmic reticulum IFN stimulator; Endoplasmic reticulum interferon stimulator; ERIS; hMITA; hSTING; Mediator of IRF3 activation; mitochondrial mediator of IRF3 activation; N-terminal methionine-proline-tyrosine-serine plasma membrane tetraspanner; Stimulator of interferon genes protein; tm173; Transmembrane protein 173
Gene Aliases: ERIS; hMITA; hSTING; MITA; MPYS; NET23; SAVI; STING; STING1; TMEM173
UniProt ID: (Human) Q86WV6
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 340061

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support