Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 3
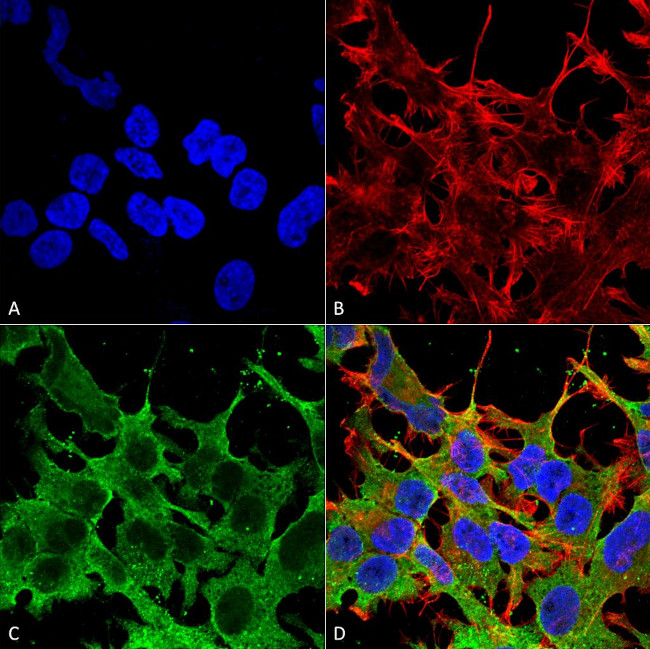
SUR2A Antibody (11570-100UG) in ICC/IF
Product Details
11570-100UG
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Sulfonylurea receptors (SUR) are membrane proteins which are the molecular targets of the sulfonylurea class of anti-diabetic drugs whose mechanism of action is to promote insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. More specifically, SUR proteins are subunits of the inward-rectifier potassium ion channels Kir6.x (6.1 and 6.2). The association of four Kir6.x and four SUR subunits form an ion conducting channel commonly referred to as the KATP channel. The primary function of the sulfonylurea receptor is to sense intracellular levels of the nucleotides ATP and ADP and in response facilitate the open or closing its associated Kir6.x potassium channel. Hence the KATP channel monitors the energy balance within the cell.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9; ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 9; ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 9; FLJ36852; Sulfonylurea receptor 2; sulfonylurea-binding protein 2
Gene Aliases: Abcc9; AI414027; AI449286; Sur2; SUR2A; SUR2B
UniProt ID: (Rat) Q63563, (Mouse) P70170
Entrez Gene ID: (Rat) 25560, (Mouse) 20928

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support