Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
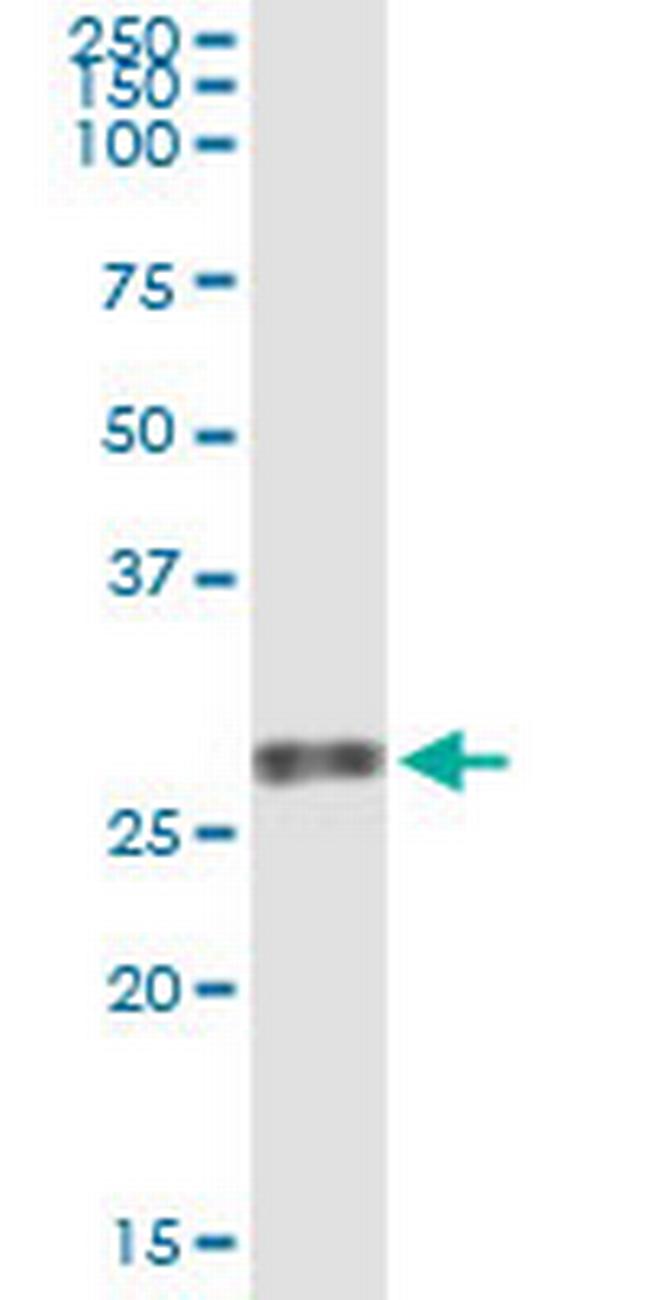
H00007423-M03
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Immunogen sequence: DAPGHQRKVV SWIDVYTRAT CQPREVVVPL TVELMGTVAK QLVPSCVTVQ RCGGCCPDDG LECVPTGQHQ VRMQILMIRY PSSQLGEMSL EEHSQCECRP KKKDSAVKPD
Target Information
Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) are a family of closely related growth factors having a conserved pattern of eight cysteine residues and sharing common VEGF receptors. VEGFs stimulate endothelial cells, induce angiogenesis, promote cell migration, increase vascular permeability, and inhibit apoptosis. VEGFB has structural similarities to VEGF and PIGF and is frequently co-expressed with VEGF. There are two alternatively spliced isoforms of VEGFB: VEGFB 167 and VEGFB 186. VEGFB 167, a highly basic heparin-binding protein, remains with the cell or extracellular matrix whereas, VEGFB 186 is readily secreted. VEGFB stimulates endothelial cell proliferation. VEGFB binds to the tyrosine kinase receptor VEGFR1 (flt1) and does not bind to VEGFR2. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor B is widely expressed but is most abundant in heart, skeletal muscle, and pancreas. It has been suggested that VEGFB expression in human primary breast cancers is associated with lymph node metastasis. The genes that encode VEGFB have been mapped to chromosome 11q13.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Vascular endothelial growth factor B; VEGF-B; VEGF-related factor; VRF
Gene Aliases: VEGFB; VEGFL; VRF
UniProt ID: (Human) P49765
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 7423

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support