Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
FIGURE: 1 / 1
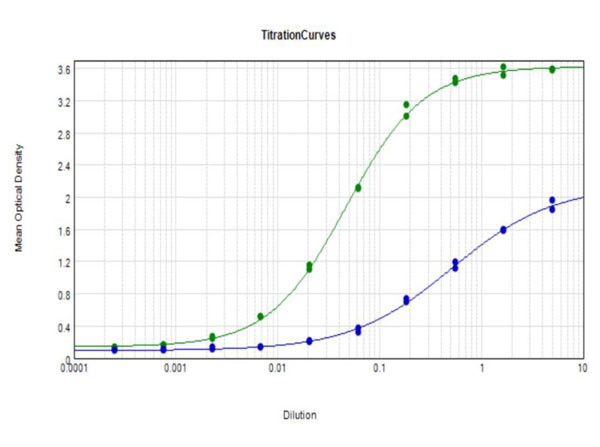
beta Amyloid 42 Antibody (600-401-J54) in ELISA

Product Details
600-401-J54
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use.
A BLAST analysis was used to suggest reactivity with human, sheep, rabbit, canine, bovne, pig, guinea pig, and monkey based on 100% sequence homology. This antibody will not react with AB40. Cross-reactivity with Beta Amyloid from other sources has not been determined.
Target Information
Amyloid beta peptide (Abeta/Beta-amyloid) is the major constituent of amyloid plaques in the brains of individuals afflicted with Alzheimer's disease. Abeta peptide is 40-43 amino acids long and generated from the beta-amyloid precursor protein (beta APP) in a two-step process. The first step involves cleavage of the extracellular, amino-terminal domain of beta APP. Protein cleavage is performed by an aspartyl protease, beta-secretase (BACE) which is synthesized as a propeptide and must be modified to the mature and active form by the prohormone convertase, furin. Beta APP cleavage by the mature form of BACE results in the cellular secretion of a segment of beta APP, and a membrane-bound remnant. The remnant protein is processed by another protease, gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase cleaves an intra-membrane site in the carboxyl-terminal domain of beta APP, thus generating the amyloid beta peptide. Gamma-secretase is believed to be a multi-subunit complex containing presenilin-1 and 2 as central components. The transmembrane glycoprotein, nicastrin, is associated with presinilins and has been found to bind to the carboxyl-terminus of beta APP and helps to modulate the production of the amyloid beta peptide. Abeta is an extracellular filamentous protein component of amyloid cores, neuritic plaques and is also found as a deposit in neurofibrillary tangles. Alzheimer’s disease, the most common cause of senile dementia, is characterized by abnormal filamentous protein deposits in the brain. Beta amyloid deposits are also detected in Lewy body dementia, Down’s syndrome, amyloidosis (Dutch type), cerebroarterial amyloidosis (cerebral amyloid angiopathy) and in the Guam Parkinson-Dementia complex.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: ABPP; AG; Alzheimer disease; Alzheimer disease amyloid A4 protein homolog; Alzheimer disease amyloid protein; Amyloid; amyloid A4; Amyloid b; Amyloid beta; amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein; amyloid beta A4 protein; Amyloid precursor protein; Amyloid β; Amyloid-beta (A4) precursor protein; Amyloid-beta A4 protein; Amyloid-beta precursor protein; Amyloidogenic glycoprotein; APP; APPI; appican; beta-amyloid peptide; beta-amyloid peptide(1-40); beta-amyloid peptide(1-42); beta-amyloid precursor protein; Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide; CTF gamma; CTF-alpha; CVAP; OTTHUMP00000096096; Pan-Abeta; peptidase nexin-II; PN-II; PreA4; PreA4 751; protease nexin II; Protease nexin-II; testicular tissue protein Li 2
Gene Aliases: A4; AAA; ABETA; ABPP; AD1; Adap; Ag; APP; APPI; betaApp; CTFgamma; CVAP; E030013M08Rik; PN-II; PN2
UniProt ID: (Human) P05067, (Rat) P08592, (Mouse) P12023
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 351, (Rat) 54226, (Mouse) 11820

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support