Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Invitrogen
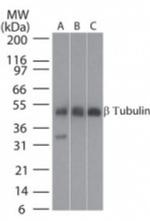
beta Tubulin Polyclonal Antibody
FIGURE: 1 / 15
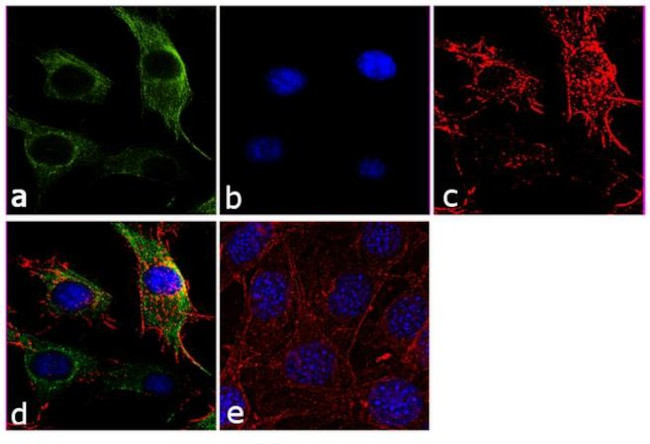
beta Tubulin Antibody (PA1-41331) in ICC/IF

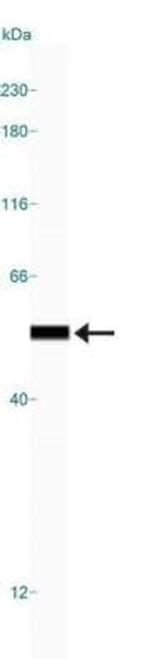

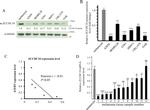
Product Details
PA1-41331
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Suggested positive control: antigen standard for TUBB2A (transient overexpression lysate), human brain protein.
Target Information
Beta tubulins are one of two core protein families (alpha and beta tubulins) that heterodimerize and assemble to form microtubules. Beta-III tubulin is primarily expressed in neurons and may be involved in neurogenesis, axon guidance and maintenance. Mutations in the beta tubulin gene are the cause of congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 3. Beta-III tubulin was also detected in Sertoli cells of the testis and transiently in non-neuronal embryonic tissues. Glutamate residues at the C-terminus of beta III tubulin can be glutamylated. The precise function of such modifications is unclear. Tubulin is phosphorylated on Ser-172 by CDK1 during cell cycle progression. Ser-172 phosphorylation inhibits tubulin incorporation into microtubules.Microtubules, the major cytoskeletal elements found in all eukaryotic cells, consist of Tubulin, which is a dimer of two 55 kDa subunits: alpha and Beta. Microtubules play key roles in chromosome segregation in mitosis, intracellular transport, ciliary and flagellar bending, and structural support of the cytoskeleton. Because beta-tubulin is ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells, it is frequently used as a loading control for assays involving protein detection, such as Western blotting.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: beta 5-tubulin; beta Ib tubulin; beta tubulin 1; beta-4 tubulin; beta-4-tubulin; beta-5 tubulin; beta-tubulin; Beta-tubulin class-I; Beta-tubulin class-II; beta-tubulin class-III; Beta-tubulin class-V; Beta-tubulin class-VI; beta-tubulin T beta15 (aa 1-445); beta5-tubulin; betaIII-tubulin; c(beta)7 tubulin; class I beta-tubulin; class II beta-tubulin isotype; class IIa beta-tubulin; class IIb beta-tubulin; class III beta-tubulin; class IVa beta-tubulin; class V beta-tubulin; dJ40E16.7; dystonia 4, torsion (autosomal dominant); HSA10p15 beta-tubulin 4Q; M40 antibody; Neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin; T beta-15; TUBB; tubb beta-5; tubb2a {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TMM9}; Tubulin 5 beta; tubulin beta; Tubulin beta 4'; Tubulin beta 8 class VIII; Tubulin beta chain; Tubulin beta class IIa; Tubulin beta class V; tubulin beta MGC4083; tubulin beta-1; Tubulin beta-1 chain; Tubulin beta-2 chain; Tubulin beta-2A chain; Tubulin beta-2B chain; Tubulin beta-3 chain; Tubulin beta-4 chain; Tubulin beta-4A chain; Tubulin beta-5 chain; Tubulin beta-6 chain; Tubulin beta-7 chain; Tubulin beta-8 chain; Tubulin beta-III; tubulin, beta 1 class VI; tubulin, beta 2; tubulin, beta 2A; tubulin, beta 2A class IIa; tubulin, beta 2B class IIb; tubulin, beta 3; tubulin, beta 3 class III; tubulin, beta 4; tubulin, beta 4 class IVa; tubulin, beta 4A class IVa; tubulin, beta 5; tubulin, beta 6 class V; tubulin, beta class I; tubulin, beta polypeptide; tubulin, beta polypeptide 2; tubulin, beta polypeptide paralog; tubulin, beta, 3; tubulin, beta, 4; tubulin, beta, 5; unnamed protein product
Gene Aliases: 2310057H16Rik; 2410129E14Rik; 2810484G07Rik; 3200002H15Rik; AA408537; AI325297; AI596182; B130022C14Rik; bA506K6.1; bA631M21.2; BB220206; beta-4; beta-5; brdp; CDCBM; CDCBM1; CDCBM5; CDCBM6; CFEOM3; CFEOM3A; CSCSC1; DYT4; FEOM3; HsT1601; M(beta)1; M(beta)2; M(beta)3; M(beta)4; M(beta)5; M(beta)6; M40; OK/SW-cl.56; OOMD; OOMD2; PMGYSA; RGD1305887; RGD1309427; TUBB; TUBB-5; TUBB1; TUBB2; TUBB2A; TUBB2B; TUBB3; TUBB4; TUBB4A; TUBB5; TUBB6; TUBB8; XELAEV_18039222mg; XLOT
UniProt ID: (Chicken) P09244, (Human) P07437, (Bovine) Q2KJD0, (Chicken) P09207, (Human) Q9H4B7, (Human) Q13885, (Bovine) Q6B856, (Human) Q9BVA1, (Chicken) P32882, (Bovine) Q2T9S0, (Human) Q13509, (Bovine) Q3ZBU7, (Human) P04350, (Human) Q9BUF5, (Chicken) P09653, (Bovine) Q2HJ81, (Human) Q3ZCM7, (Mouse) A2AQ07, (Rat) P85108, (Mouse) Q7TMM9, (Mouse) Q9CWF2, (Rat) Q3KRE8, (Mouse) Q9ERD7, (Rat) Q4QRB4, (Mouse) Q9D6F9, (Mouse) P99024, (Rat) P69897, (Mouse) Q922F4, (Xenopus) Q91575
Entrez Gene ID: (Chicken) 396254, (Dog) 474830, (Human) 203068, (Bovine) 615087, (Chicken) 396427, (Bovine) 541271, (Human) 81027, (Cat) 100188929, (Dog) 485950, (Human) 7280, (Chicken) 768337, (Dog) 478702, (Bovine) 281555, (Human) 347733, (Chicken) 420883, (Chicken) 431043, (Dog) 102154194, (Bovine) 768070, (Human) 10381, (Dog) 100855815, (Bovine) 540236, (Human) 10382, (Human) 84617, (Chicken) 421037, (Bovine) 534206, (Dog) 480213, (Human) 347688, (Mouse) 545486, (Rat) 679312, (Rat) 498736, (Mouse) 22151, (Mouse) 73710, (Rat) 291081, (Mouse) 22152, (Rat) 246118, (Rat) 29213, (Mouse) 22153, (Mouse) 22154, (Rat) 29214, (Mouse) 67951, (Rat) 307351, (Xenopus) 380418

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support