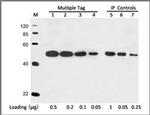
Product References
Structure and function analysis of a CC-NBS-LRR protein AT1G12290.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Huang J,Wu X,Sun K,Gao Z
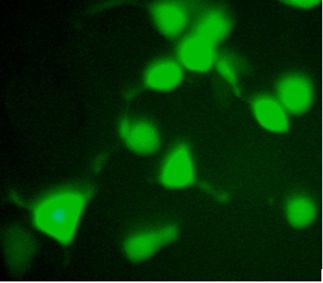
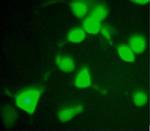
Nucleotide-binding site (NBS) and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) receptors (NLRs) play important roles in plant immunity. The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains about 150 genes encoding NLR proteins, but few of them have been studied. We transiently expressed a series of NBS-LRR proteins in the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana, and found that the CC-NBS-LRR protein (AT1G12290) was able to trigger cell death, a characterized function for the activation of an NLR protein. We observed that the YFP-t
Fri Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2021
APC/CFZR-1 regulates centrosomal ZYG-1 to limit centrosome number.
Journal of cell science
Medley JC,DiPanni JR,Schira L,Shaffou BM,Sebou BM,Song MH
Aberrant centrosome numbers are associated with human cancers. The levels of centrosome regulators positively correlate with centrosome number. Thus, tight control of centrosome protein levels is critical. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the anaphasepromoting complex/cyclosome and its co-activator FZR-1 (APC/ CFZR-1),aubiquitinligase,negativelyregulatescentrosomeassembly through SAS-5 degradation. In this study, we report the C. elegans ZYG-1 (Plk4 in humans) as a potential substrate of APC/CFZR-1. I
Thu Jul 15 00:00:00 EDT 2021
Regulation of Aluminum Resistance in Arabidopsis Involves the SUMOylation of the Zinc Finger Transcription Factor STOP1.
The Plant cell
Fang Q,Zhang J,Zhang Y,Fan N,van den Burg HA,Huang CF
Tue Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2020
A Cycle of Ubiquitination Regulates Adaptor Function of the Nedd4-Family Ubiquitin Ligase Rsp5.
Current biology : CB
MacDonald C,Shields SB,Williams CA,Winistorfer S,Piper RC
Mon Feb 03 00:00:00 EST 2020
Molecular Characterization of Differences between the Tomato Immune Receptors Flagellin Sensing 3 and Flagellin Sensing 2.
Plant physiology
Roberts R,Liu AE,Wan L,Geiger AM,Hind SR,Rosli HG,Martin GB
Sat Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Bacterial type III effector protein HopQ inhibits melanoma motility through autophagic degradation of vimentin.
Cell death & disease
Park SH,Yoon SJ,Choi S,Kim JS,Lee MS,Lee SJ,Lee SH,Min JK,Son MY,Ryu CM,Yoo J,Park YJ
Malignant melanoma is a fatal disease that rapidly spreads to the whole body. Treatments have limited efficiency owing to drug resistance and various side effects. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pto) is a model bacterial pathogen capable of systemic infection in plants. Pto injects the effector protein HopQ into the plant cytosol via a type III secretion machinery and suppresses the host immunity. Intriguingly, host plant proteins regulated by HopQ are conserved even in humans and conferred in
Tue Apr 14 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Divergent receptor proteins confer responses to different karrikins in two ephemeral weeds.
Nature communications
Sun YK,Yao J,Scaffidi A,Melville KT,Davies SF,Bond CS,Smith SM,Flematti GR,Waters MT
Wildfires can encourage the establishment of invasive plants by releasing potent germination stimulants, such as karrikins. Seed germination of Brassica tournefortii, a noxious weed of Mediterranean climates, is strongly stimulated by KAR1, the archetypal karrikin produced from burning vegetation. In contrast, the closely-related yet non-fire-associated ephemeral Arabidopsis thaliana is unusual because it responds preferentially to KAR2. The α/β-hydrolase KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE 2 (KAI2)
Mon Mar 09 00:00:00 EDT 2020
The Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF34 Protein Interacts and Stabilizes HIF-2α via Binding to the HIF-2α bHLH and PAS Domains.
Journal of virology
Haque M,Kousoulas KG
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) play important roles in the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) life cycle. KSHV is the causative agents of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and other AIDS related malignancies. Kaposi's sarcoma is a highly vascular tumor which preferentially develops in the lower extremities of the body where blood vessels are often poorly oxygenated. The main cellular responses to hypoxia are mediated mainly by two isoforms of HIF HIF-1α and HIF-2α. Both
Sun Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Mai1 Protein Acts Between Host Recognition of Pathogen Effectors and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling.
Molecular plant-microbe interactions : MPMI
Roberts R,Hind SR,Pedley KF,Diner BA,Szarzanowicz MJ,Luciano-Rosario D,Majhi BB,Popov G,Sessa G,Oh CS,Martin GB
The molecular mechanisms acting between host recognition of pathogen effectors by nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptor (NLR) proteins and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascades are unknown. MAPKKKα (M3Kα) activates MAPK signaling leading to programmed cell death (PCD) associated with NLR-triggered immunity. We identified a tomato M3Kα-interacting protein SlMai1 that has 80% amino acid identity with brassinosteroid kinase 1 (AtBsk1). SlMai1 has a
Fri Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Sumoylation regulates the stability and nuclease activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dna2.
Communications biology
Ranjha L,Levikova M,Altmannova V,Krejci L,Cejka P
Dna2 is an essential nuclease-helicase that acts in several distinct DNA metabolic pathways including DNA replication and recombination. To balance these functions and prevent unscheduled DNA degradation Dna2 activities must be regulated. Here we show that Dna2 function is controlled by sumoylation. We map the sumoylation sites to the N-terminal regulatory domain of Dna2 and show that in vitro sumoylation of recombinant Dna2 impairs its nuclease but not helicase activity. In cells the total lev
Mon Apr 20 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Autophagy resists EMT process to maintain retinal pigment epithelium homeostasis.
International journal of biological sciences
Feng H,Zhao X,Guo Q,Feng Y,Ma M,Guo W,Dong X,Deng C,Li C,Song X,Han S,Cao L
Proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) is the most serious fibrous complication that causes vision loss after intraocular surgery and there is currently no effective treatment in clinical. Autophagy is an important cell biological mechanism in maintaining the homeostasis of tissues and cells resisting the process of EMT. However it is still unclear whether autophagy could resist intraocular fibrosis and prevent PVR progression. In this study we investigated the expression of mesenchymal biomarker
Mon Jan 20 00:00:00 EST 2020
A Quick HYL1-Dependent Reactivation of MicroRNA Production Is Required for a Proper Developmental Response after Extended Periods of Light Deprivation.
Developmental cell
Achkar NP,Cho SK,Poulsen C,Arce AL,Re DA,Giudicatti AJ,Karayekov E,Ryu MY,Choi SW,Harholt J,Casal JJ,Yang SW,Manavella PA
Light is the most influential environmental stimulus for plant growth. In response to deficient light plants reprogram their development to adjust their growth in search for a light source. A fine reprogramming of gene expression orchestrates this adaptive trait. Here we show that plants alter microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis in response to light transition. When plants suffer an unusual extended period of light deprivation the miRNA biogenesis factor HYPONASTIC LEAVES 1 (HYL1) is degraded but a
Mon Jul 16 00:00:00 EDT 2018
HSF1 critically attunes proteotoxic stress sensing by mTORC1 to combat stress and promote growth.
Nature cell biology
Su KH,Cao J,Tang Z,Dai S,He Y,Sampson SB,Benjamin IJ,Dai C
To cope with proteotoxic stress cells attenuate protein synthesis. However the precise mechanisms underlying this fundamental adaptation remain poorly defined. Here we report that mTORC1 acts as an immediate cellular sensor of proteotoxic stress. Surprisingly the multifaceted stress-responsive kinase JNK constitutively associates with mTORC1 under normal growth conditions. On activation by proteotoxic stress JNK phosphorylates both RAPTOR at S863 and mTOR at S567 causing partial disintegration o
Sun May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2016
The E3 ubiquitin protein ligase MDM2 dictates all-trans retinoic acid-induced osteoblastic differentiation of osteosarcoma cells by modulating the degradation of RARα.
Oncogene
Ying M,Zhang L,Zhou Q,Shao X,Cao J,Zhang N,Li W,Zhu H,Yang B,He Q
Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) has a critical role in the differentiation process of osteosarcoma cells induced by all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). However degradation of RARα through ubiquitin proteasome pathway weakens the differentiation efficiency of osteosarcoma cells. In this study we discover that murine double minute-2 (MDM2) acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to target RARα for degradation. We observe that MDM2 is required for RARα polyubiquitination and proteaso
Thu Aug 18 00:00:00 EDT 2016
Voltage-gated calcium channels of Paramecium cilia.
The Journal of experimental biology
Lodh S,Yano J,Valentine MS,Van Houten JL
Paramecium cells swim by beating their cilia and make turns by transiently reversing their power stroke. Reversal is caused by Ca entering the cilium through voltage-gated Ca (Ca) channels that are found exclusively in the cilia. As ciliary Ca levels return to normal the cell pivots and swims forward in a new direction. Thus the activation of the Ca channels causes cells to make a turn in their swimming paths. For 45years the physiological characteristics of the Paramecium ciliary Ca channels ha
Sat Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2016
Expression of Cucumber mosaic virus suppressor 2b alters FWA methylation and its siRNA accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Biology open
Hamera S,Yan Y,Song X,Chaudhary SU,Murtaza I,Su L,Tariq M,Chen X,Fang R
The Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) suppressor 2b co-localizes with AGO4 in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of Arabidopsis thaliana Biochemical fractionation of A. thaliana cellular extracts revealed that 2b and AGO4 coexist in multiple size exclusions. 2b transgenic A. thaliana exhibited an enhanced accumulation of 24nt siRNAs from flowering wageningen (FWA) and other heterochromatic loci. These plants also exhibited hypo-methylation of an endogenous- as well as transgene-FWA promoter at non-CG s
Tue Nov 15 00:00:00 EST 2016
The E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP mediates ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of PRMT5.
Biochimica et biophysica acta
Zhang HT,Zeng LF,He QY,Tao WA,Zha ZG,Hu CD
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is an important member of the protein arginine methyltransferase family that regulates many cellular processes through epigenetic control of target gene expression. Because of its overexpression in a number of human cancers and its essential role in cell proliferation, transformation, and cell cycle progression, PRMT5 has been recently proposed to function as an oncoprotein in cancer cells. However, how its expression is regulated in cancer cells rema
Mon Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2016
Endogenous IGFBP-3 Mediates Intrinsic Apoptosis Through Modulation of Nur77 Phosphorylation and Nuclear Export.
Endocrinology
Agostini-Dreyer A,Jetzt AE,Stires H,Cohick WS
In nontransformed bovine mammary epithelial cells, the intrinsic apoptosis inducer anisomycin (ANS) induces IGFBP-3 expression and nuclear localization and knockdown of IGFBP-3 attenuates ANS-induced apoptosis. Others have shown in prostate cancer cells that exogenous IGFBP-3 induces apoptosis by facilitating nuclear export of the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 and its binding partner, retinoid X receptor-α (RXRα). The goal of the present work was to determine whether endogenous IGFBP
Sun Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2015
qPCA: a scalable assay to measure the perturbation of protein-protein interactions in living cells.
Molecular bioSystems
Freschi L,Torres-Quiroz F,Dubé AK,Landry CR
One of the most important challenges in systems biology is to understand how cells respond to genetic and environmental perturbations. Here we show that the yeast DHFR-PCA, coupled with high-resolution growth profiling (DHFR-qPCA), is a straightforward assay to study the modulation of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) in vivo as a response to genetic, metabolic and drug perturbations. Using the canonical Protein Kinase A (PKA) pathway as a test system, we show that changes in PKA activity can
Sun Jan 27 00:00:00 EST 2013
Opposing effects of bacitracin on human papillomavirus type 16 infection: enhancement of binding and entry and inhibition of endosomal penetration.
Journal of virology
Campos SK,Chapman JA,Deymier MJ,Bronnimann MP,Ozbun MA
Cell invasion by human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) is a complex process relying on multiple host cell factors. Here we describe an investigation into the role of cellular protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) by studying the effects of the commonly used PDI inhibitor bacitracin on HPV16 infection. Bacitracin caused an unusual time-dependent opposing effect on viral infection. Enhanced cellular binding and entry were observed at early times of infection, while inhibition was observed at later ti
Sun Apr 01 00:00:00 EDT 2012
A single ubiquitin is sufficient for cargo protein entry into MVBs in the absence of ESCRT ubiquitination.
The Journal of cell biology
Stringer DK,Piper RC
ESCRTs (endosomal sorting complexes required for transport) bind and sequester ubiquitinated membrane proteins and usher them into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). As Ubiquitin (Ub)-binding proteins, ESCRTs themselves become ubiquitinated. However, it is unclear whether this regulates a critical aspect of their function or is a nonspecific consequence of their association with the Ub system. We investigated whether ubiquitination of the ESCRTs was required for their ability to sort cargo into the M
Mon Jan 24 00:00:00 EST 2011
Drosophila melanogaster Cyclin G coordinates cell growth and cell proliferation.
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
Faradji F,Bloyer S,Dardalhon-Cuménal D,Randsholt NB,Peronnet F
Mammalian Cyclins G1 and G2 are unconventional cyclins whose role in regulating the cell cycle is ambiguous. Cyclin G1 promotes G2/M cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage whereas ectopic expression of CCNG2, that encodes Cyclin G2, induces G1/S cell cycle arrest. The only Drosophila Cyclin G was previously shown to be a transcriptional regulator that interacts with the chromatin factor Corto and controls expression of the homeotic gene Abdominal B. It is very close to mammalian Cyclin G1 a
Tue Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2011