Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Specifications
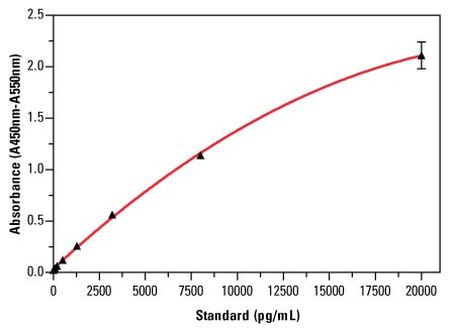
Analytical sensitivity
Assay range
Sample type/volume
Hands-on time
Time-to-result
Homogenous (no wash)
Interassay CV
Intraassay CV
Instrument
Product size
Contents
Standard
Assay Diluent concentrate
Biotinylated Detection Antibody
SAV-HRP
Wash Buffer
Chromogen
Stop Solution
Adhesive Plate Covers
Shipping conditions
Storage
Protein name
Protein family
Species (tested)
Assay kit format
Detector antibody conjugate
Label or dye
About This Kit
The Human HIF1A ELISA quantitates Hu HIF1A in human serum, plasma, or cell culture lysates. The assay will exclusively recognize both natural and recombinant Hu HIF1A.
Principle of the method
The Human HIF1A solid-phase sandwich ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is designed to measure the amount of the target bound between a matched antibody pair. A target-specific antibody has been pre-coated in the wells of the supplied microplate. Samples, standards, or controls are then added into these wells and bind to the immobilized (capture) antibody. The sandwich is formed by the addition of the second (detector) antibody, a substrate solution is added that reacts with the enzyme-antibody-target complex to produce measurable signal. The intensity of this signal is directly proportional to the concentration of target present in the original specimen.
Rigorous validation
Each manufactured lot of this ELISA kit is quality tested for criteria such as sensitivity, specificity, precision, and lot-to-lot consistency. See manual for more information on validation.
HIF1-alpha (HIF1A) is a subunit of HIF1, which is a transcription factor found in mammalian cells cultured under reduced oxygen tension. HIF-1 is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha and beta subunit, both belonging to the basic-helix-loop-helix Per-aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-Sim (PAS) family of transcription factors. HIF1 functions as a transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia. Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, HILPDA, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. HIF1-alpha regulates hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Hypoxia which induces p53 protein accumulation, directly interacts with HIF1-alpha and reduces hypoxia-induced expression of HIF1-alpha by promoting MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation under hypoxic conditions. Recent studies suggest that induction of NOX4 by HIF1-alpha contributes to maintain ROS levels after hypoxia and hypoxia-induced proliferation. In humans, it is located on the q arm of chromosome 14. The C-terminal of HIF1A binds to p300. p300/CBP-HIF complexes participate in the induction of hypoxia-responsive genes, including VEGF. Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Gene aliases : BHLHE78, HIF-1-alpha, HIF-1A, HIF-1alpha, HIF1, HIF1-ALPHA, HIF1A, MOP1, PASD8
Gene ID : (Human) 3091
Gene symbol : HIF1A
Protein Aliases : ARNT interacting protein, ARNT-interacting protein, Basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP1, bHLHe78, Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 78, HIF-1-alpha, hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor), hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha isoform I.3, hypoxia-inducible factor 1, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, hypoxia-inducible factor1alpha, Member of PAS protein 1, member of PAS superfamily 1, PAS domain-containing protein 8
UniProt ID (Human) Q16665

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support