Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Product Details
14-8989-80
Species
Published species
Expression System
Amino acid sequence
Molecular weight
Class
Type
Purity
Endotoxin concentration
Activity
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Description: The platelet-derived growth factor AA (PDGF-AA) is a member of the PDGF family. The PDGF proteins are derived from four genes (PDGF-A, -B, -C, and -D) that form four disulfide-linked homodimers (PDGF-AA, -BB, -CC, and -DD) and one heterodimer (PDGF-AB). PDGF-AA plays an important role as a mitogen for a number of cell types. Recombinant Mouse PDGF-AA produced in E.coli is a non-glycosylated homodimer of 126 amino acids with a molecular weight of 28.9 kDa.
Applications Reported: Recombinant mouse PDGF-AA is biologically active and can promote proliferation of mouse 3T3 cells in culture.
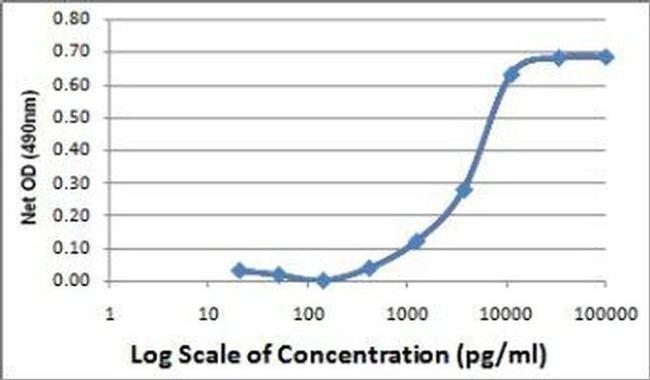
Applications Tested: This reagent has been tested in bioassays using the mouse cell line 3T3. The ED50 measured in a 3T3 proliferation assay is typically 10 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of approximately 1 x10e5 Units/mg.
Bioactivity: The ED50 measured in a 3T3 proliferation assay is typically 9.7 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of approximately 1 x10e5 Units/mg.
Endotoxin: Less than 0.1 ng/µg cytokine as determined by the LAL assay. Purity: >97% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Storage and handling: For best recovery, quick-spin vial prior to opening. Use in a sterile environment.
Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Target Information
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) was discovered as a major mitogenic factor present in serum but absent from plasma. It was found to be secreted from the alpha -granules of platelets activated during the coagulation of blood to form serum. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that PDGF is not one molecule but three, each a dimeric combination of two distinct but structurally related peptide chains designated A and B. The dimeric isoforms PDGF-AA, AB and BB are differentially expressed in various cell types and their effects are mediated through two distinct receptors, termed alpha and beta. Differences exist in isoform binding to each receptor. In general, PDGF isoforms are potent mitogens for connective tissue cells, including dermal fibroblasts, glial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells and some epithelial and endothelial cells. In addition to its activity as a mitogen, PDGF is chemotactic for fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, neutrophils and mononuclear cells. Other reported activities for PDGF include stimulation of granule release by neutrophils and monocytes, facilitation of steroid synthesis by Leydig cells, stimulation of neutrophil phagocytosis, inhibition of natural killer (NK) cell activity, stimulation of collagen synthesis, modulation of thrombospondin expression and secretion, stimulation of collagenase activity and secretion, induction of contraction of rat aorta strips in vitro, and transient induction of T cell IL-2 secretion accompanied by a down-regulation of IL-4 and IFN-gamma production, temporary effects that may allow clonal expansion of antigen-activated B and T helper lymphocytes prior to differentiation. PDGF also appears to be ubiquitous in neurons throughout the CNS, where it is suggested to play an important role in neuron survival and regeneration, and in mediation of glial cell proliferation and differentiation.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: H-PDGF-AA; PDGF subunit A; PDGF-1; Platelet-derived growth factor A chain; Platelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide; Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A
Gene Aliases: Pdgfa
UniProt ID: (Mouse) P20033
Entrez Gene ID: (Mouse) 18590

We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support