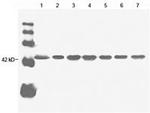
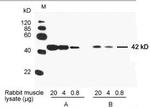
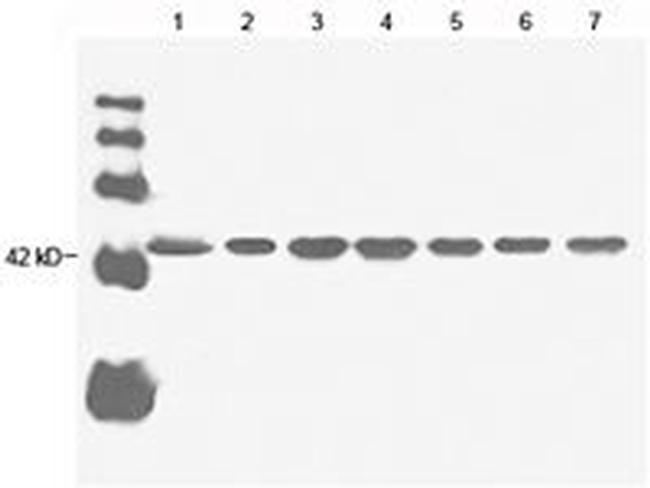
Product References
Inactivation of the AMPK-GATA3-ECHS1 Pathway Induces Fatty Acid Synthesis That Promotes Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Growth.
Cancer research
Qu YY,Zhao R,Zhang HL,Zhou Q,Xu FJ,Zhang X,Xu WH,Shao N,Zhou SX,Dai B,Zhu Y,Shi GH,Shen YJ,Zhu YP,Han CT,Chang K,Lin Y,Zang WD,Xu W,Ye DW,Zhao SM,Zhao JY
The tumorigenic role and underlying mechanisms of lipid accumulation, commonly observed in many cancers, remain insufficiently understood. In this study, we identified an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3)-enoyl-CoA hydratase short-chain 1 (ECHS1) pathway that induces lipid accumulation and promotes cell proliferation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Decreased expression of ECHS1, which is responsible for inactivation of fatty acid (FA) oxidation and ac
Wed Jan 15 00:00:00 EST 2020
Coronavirus endoribonuclease targets viral polyuridine sequences to evade activating host sensors.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Hackbart M,Deng X,Baker SC
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are positive-sense RNA viruses that can emerge from endemic reservoirs and infect zoonotically, causing significant morbidity and mortality. CoVs encode an endoribonuclease designated EndoU that facilitates evasion of host pattern recognition receptor MDA5, but the target of EndoU activity was not known. Here, we report that EndoU cleaves the 5'-polyuridines from negative-sense viral RNA, termed PUN RNA, which is the product of polyA-templated RNA synthesis. Using a virus co
Tue Apr 07 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Dual functions of Rack1 in regulating Hedgehog pathway.
Cell death and differentiation
Li Y,Sun X,Gao D,Ding Y,Liu J,Chen J,Luo J,Zhang J,Liu Q,Zhou Z
Sun Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
The Pyrimidine Analog FNC Potently Inhibits the Replication of Multiple Enteroviruses.
Journal of virology
Xu N,Yang J,Zheng B,Zhang Y,Cao Y,Huan C,Wang S,Chang J,Zhang W
Thu Apr 16 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Silver nanoparticles stimulate osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through activation of autophagy.
Nanomedicine (London, England)
He W,Zheng Y,Feng Q,Elkhooly TA,Liu X,Yang X,Wang Y,Xie Y
Aim: Previously, different results have been achieved regarding effects of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) on osteogenesis of stem cells and the mechanisms have not been disclosed yet, which are quite important for potential application of Ag NPs in bone reconstruction. Materials & methods: Effects of Ag NPs on osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) with underlying mechanisms were investigated. Results: Ag NPs at 2.5 and 5 µg/ml increased osteogenic proteins expression and
Sat Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2020
Respiratory defects in the CrtapKO mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology
Dimori M,Heard-Lipsmeyer ME,Byrum SD,Mackintosh SG,Kurten RC,Carroll JL,Morello R
Respiratory disease is a leading cause of mortality in patients with Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI), a connective tissue disease that causes severely reduced bone mass and is most commonly caused by dominant mutations in type I collagen genes. Previous studies proposed that impaired respiratory function in OI patients was secondary to skeletal deformities however recent evidence suggests the existence of a primary lung defect. Here, we analyzed the lung phenotype of CrtapKO mice, a mouse model of
Wed Apr 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Neuroserpin regulates human T cell-T cell interactions and proliferation through inhibition of tissue plasminogen activator.
Journal of leukocyte biology
Loef EJ,Brooks AES,Lorenz N,Birch NP,Dunbar PR
T cells play a key role in mounting an adaptive immune response. T cells are activated upon recognition of cognate Ag presented by an APC. Subsequently, T cells adhere to other activated T cells to form activation clusters, which lead to directed secretion of cytokines between communicating cells. T cell activation clusters have been implicated in regulating activation, proliferation, and memory formation in T cells. We previously reported the expression of the protease inhibitor neuroserpin by
Wed Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2020
CDK9 inhibitors reactivate p53 by downregulating iASPP.
Cellular signalling
Wu J,Liang Y,Tan Y,Tang Y,Song H,Wang Z,Li Y,Lu M
Loss of p53's tumor-suppressive function, either via TP53 mutation or hyperactive p53 inhibitory proteins, is one of the most frequent events in the development of human cancer. Here, we describe a strategy of pharmacologically inhibiting iASPP, a negative regulator of p53, to restore wild-type p53's tumor-suppressive function. iASPP knockdown in the colon cancer cell line HCT116 efficiently promoted p53's transcriptional activity and induced p53-dependent cell death, suggesting a key role for i
Sun Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2020
Lentiviral Gene Therapy for Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Type 3, Caused by UNC13D Genetic Defects.
Human gene therapy
Takushi SE,Paik NY,Fedanov A,Prince C,Doering CB,Spencer HT,Chandrakasan S
Mon Jun 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Signature of high altitude adaptation in the gluteus proteome of the yak.
Journal of experimental zoology. Part B, Molecular and developmental evolution
Xin JW,Chai ZX,Zhang CF,Zhang Q,Zhu Y,Cao HW,Ji CY,Chen XY,Jiang H,Zhong JC,Ji QM
Tue Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
The Zscan4-Tet2 Transcription Nexus Regulates Metabolic Rewiring and Enhances Proteostasis to Promote Reprogramming.
Cell reports
Cheng ZL,Zhang ML,Lin HP,Gao C,Song JB,Zheng Z,Li L,Zhang Y,Shen X,Zhang H,Huang Z,Zhan W,Zhang C,Hu X,Sun YP,Jiang L,Sun L,Xu Y,Yang C,Ge Y,Zhao Y,Liu X,Yang H,Liu P,Guo X,Guan KL,Xiong Y,Zhang M,Ye D
Tue Jul 14 00:00:00 EDT 2020
DART-seq: an antibody-free method for global m6A detection.
Nature methods
Meyer KD
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a widespread RNA modification that influences nearly every aspect of the messenger RNA lifecycle. Our understanding of m6A has been facilitated by the development of global m6A mapping methods, which use antibodies to immunoprecipitate methylated RNA. However, these methods have several limitations, including high input RNA requirements and cross-reactivity to other RNA modifications. Here, we present DART-seq (deamination adjacent to RNA modification targets), an ant
Sun Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2019
Transposable elements drive widespread expression of oncogenes in human cancers.
Nature genetics
Jang HS,Shah NM,Du AY,Dailey ZZ,Pehrsson EC,Godoy PM,Zhang D,Li D,Xing X,Kim S,O'Donnell D,Gordon JI,Wang T
Transposable elements (TEs) are an abundant and rich genetic resource of regulatory sequences1-3. Cryptic regulatory elements within TEs can be epigenetically reactivated in cancer to influence oncogenesis in a process termed onco-exaptation4. However, the prevalence and impact of TE onco-exaptation events across cancer types are poorly characterized. Here, we analyzed 7,769 tumors and 625 normal datasets from 15 cancer types, identifying 129 TE cryptic promoter-activation events involving 106 o
Mon Apr 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Author Correction: Transposable elements drive widespread expression of oncogenes in human cancers.
Nature genetics
Jang HS,Shah NM,Du AY,Dailey ZZ,Pehrsson EC,Godoy PM,Zhang D,Li D,Xing X,Kim S,O'Donnell D,Gordon JI,Wang T
Transposable elements (TEs) are an abundant and rich genetic resource of regulatory sequences1-3. Cryptic regulatory elements within TEs can be epigenetically reactivated in cancer to influence oncogenesis in a process termed onco-exaptation4. However, the prevalence and impact of TE onco-exaptation events across cancer types are poorly characterized. Here, we analyzed 7,769 tumors and 625 normal datasets from 15 cancer types, identifying 129 TE cryptic promoter-activation events involving 106 o
Wed May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Miro1 Marks Parkinson's Disease Subset and Miro1 Reducer Rescues Neuron Loss in Parkinson's Models.
Cell metabolism
Hsieh CH,Li L,Vanhauwaert R,Nguyen KT,Davis MD,Bu G,Wszolek ZK,Wang X
The identification of molecular targets and pharmacodynamic markers for Parkinson's disease (PD) will empower more effective clinical management and experimental therapies. Miro1 is localized on the mitochondrial surface and mediates mitochondrial motility. Miro1 is removed from depolarized mitochondria to facilitate their clearance via mitophagy. Here, we explore the clinical utility of Miro1 for detecting PD and for gauging potential treatments. We measure the Miro1 response to mitochondrial d
Tue Dec 03 00:00:00 EST 2019
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis related ER membrane protein CLN8 regulates PP2A activity and ceramide levels.
Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease
Adhikari B,De Silva B,Molina JA,Allen A,Peck SH,Lee SY
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) are a group of inherited neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorders. CLN8 deficiency causes a subtype of NCL referred to as CLN8 disease. CLN8 is an ER resident protein with unknown function; however a role in ceramide metabolism has been suggested. In this report we identified PP2A and its biological inhibitor I2PP2A as interacting proteins of CLN8. PP2A is one of the major serine/threonine phosphatases in cells and governs a wide range of signaling
Fri Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2019
Specific neural phase relation of serotonin and dopamine modulate the testicular activity in Japanese quail.
Journal of cellular physiology
Banerjee S,Chaturvedi CM
Specific phase relation of serotonin and dopamine modulate the hypothalamo-hypophyseal-gonadal axis as well as photosexual responses in Japanese quail but the effect of these specific phase relations on testicular activity and steroidogenesis is not yet been investigated. We hypothesized that temporal phase relation induced alteration in local testicular gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) and their receptor system may modulate the testicular activity and
Fri Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2019
Acacetin-induced cell apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells: Evidence for the role of muscarinic M3 receptor.
Phytotherapy research : PTR
Sun F,Li D,Wang C,Peng C,Zheng H,Wang X
Aacacetin a plant flavone has shown antitumor efficacy recently. However its associated mechanisms are poorly known. We hypothesized that the muscarinic M3 receptor (M R) which is highly expressed in some cancer tissue is related to the antitumor effect of acacetin in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells. Our results showed that 12.5- to 200-µM acacetin inhibited cell viability in dose- and time-dependent manners in HNSCC cells but a relative higher concentration was needed
Wed May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Ketamine normalizes binge drinking-induced defects in glutamatergic synaptic transmission and ethanol drinking behavior in female but not male mice.
Neuropharmacology
Crowley NA,Magee SN,Feng M,Jefferson SJ,Morris CJ,Dao NC,Brockway DF,Luscher B
Ketamine is a fast acting experimental antidepressant with significant therapeutic potential for emotional disorders such as major depressive disorder and alcohol use disorders. Of particular interest is binge alcohol use which during intermittent withdrawal from drinking involves depressive-like symptoms reminiscent of major depressive disorder. Binge drinking has been successfully modeled in mice with the Drinking in the Dark (DID) paradigm which involves daily access to 20% ethanol for a limi
Wed May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
WT1 regulates cyclin A1 expression in K562 cells.
Oncology reports
Pandey S,Moazam M,Ghimirey N,Kuerbitz SJ,Fraizer GC
The restricted expression of Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) and cyclin A1 (CCNA1) in normal tissues, as opposed to their abnormal expression in leukemia demonstrates the applicability of WT1 and CCNA1 as cancer antigens for immunotherapy, and as markers for prognosis and relapse. In this study, the WT1 and CCNA1 mRNA levels were found to be elevated in bone marrow samples from pediatric acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL or AML‚M3) patients, and to be quite varied in pediatric acute lymphocy
Fri Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Generating and evaluating type I interferon receptor-deficient and feline TMPRSS2-expressing cells for propagating serotype I feline infectious peritonitis virus.
Virology
Mettelman RC,O'Brien A,Whittaker GR,Baker SC
Fri Nov 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
GPER stabilizes F-actin cytoskeleton and activates TAZ via PLCβ-PKC and Rho/ROCK-LIMK-Cofilin pathway.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Wang Z,Sun L,Liang S,Liu ZC,Zhao ZY,Yang J,Wang D,Yang DQ
Actin is a highly abundant cytoskeletal protein that is essential for all eukaryotic cells and participates in many structural and functional roles. It has long been noted that estrogen affects cellular morphology. However recent studies observed that both estrogen and tamoxifen induce a remarkable cytoskeletal remodeling independent of ER. In addition to ER G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER also known as GPR30) also binds to estrogen with high affinity and mediates intracellular estro
Tue Aug 27 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Amazonian Phlebovirus (Bunyaviridae) potentiates the infection of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis: Role of the PKR/IFN1/IL-10 axis.
PLoS neglected tropical diseases
Rath CT,Schnellrath LC,Damaso CR,de Arruda LB,Vasconcelos PFDC,Gomes C,Laurenti MD,Calegari Silva TC,Vivarini ÁC,Fasel N,Pereira RMS,Lopes UG
Leishmania parasites are transmitted to vertebrate hosts by phlebotomine sandflies and in humans may cause tegumentary or visceral leishmaniasis. The role of PKR (dsRNA activated kinase) and Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) activation in the control of Leishmania infection highlights the importance of the engagement of RNA sensors which are usually involved in the antiviral cell response in the fate of parasitism by Leishmania. We tested the hypothesis that Phlebovirus a subgroup of the Bunyaviridae
Sat Jun 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019
Autophagy Promotes Porcine Parvovirus Replication and Induces Non-Apoptotic Cell Death in Porcine Placental Trophoblasts.
Viruses
Zhang X,Xiong Y,Zhang J,Shao T,Chen S,Miao B,Wang Z,Du Q,Huang Y,Tong D
Autophagy plays important roles in the infection and pathogenesis of many viruses, yet the regulatory roles of autophagy in the process of porcine parvovirus (PPV) infection remain unclear. Herein, we show that PPV infection induces autophagy in porcine placental trophoblasts (PTCs). Induction of autophagy by rapamycin (RAPA) inhibited the occurrence of apoptotic cell death, yet promoted viral replication in PPV-infected cells; inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA or ATG5 knockdown increased cellular
Fri Dec 20 00:00:00 EST 2019
Autophagy-lysosome pathway alterations and alpha-synuclein up-regulation in the subtype of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, CLN5 disease.
Scientific reports
Adams J,Feuerborn M,Molina JA,Wilden AR,Adhikari B,Budden T,Lee SY
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) are a group of inherited neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorders. CLN5 deficiency causes a subtype of NCL referred to as CLN5 disease. CLN5 is a soluble lysosomal protein with an unclear function in the cell. Increased levels of the autophagy marker protein LC3-II have been reported in several subtypes of NCLs. In this report we examine whether autophagy is altered in CLN5 disease. We found that the basal level of LC3-II was elevated in both CLN5 disea
Thu Jan 17 00:00:00 EST 2019
Correction: RanBP9 Overexpression Accelerates Loss of Pre and Postsynaptic Proteins in the APΔE9 Transgenic Mouse Brain.
PloS one
Wang H,Wang R,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
[This corrects the article DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085484.].
Tue Feb 25 00:00:00 EST 2020
Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Rep Enhances IL-10 Production in Macrophages via Activation of p38-MAPK Pathway.
Viruses
Wu X,Wang X,Shi T,Luo L,Qiao D,Wang Z,Han C,Du Q,Tong D,Huang Y
Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) is one of the major threats to pig farms worldwide. Although PCV2 has been identified to promote IL-10 production, the detailed regulatory roles of PCV2 Rep for IL-10 production remain unclear. Herein, we first found that PCV2 Rep, rather than PCV1 Rep, enhanced IL-10 expression at the later phase of PCV2 infection in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs). Furthermore, we found that PCV2 Rep directly activated the p38-MAPK pathway to promote transcription factors N
Tue Dec 10 00:00:00 EST 2019
CAEV Vif Hijacks ElonginB/C, CYPA and Cullin5 to Assemble the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex Stepwise to Degrade oaA3Z2-Z3.
Frontiers in microbiology
Zhao Z,Li Z,Huan C,Wang H,Su X,Zhang W
Caprine arthritis encephalitis virus (CAEV) is a lentivirus that causes multisystemic chronic disorders in sheep and goats. It encodes Vif to counteract the restriction of Ovis aries A3Z2-Z3 (oaA3Z2-Z3) by inducing their degradation. Nevertheless, the mechanisms underlying the interplay between CAEV Vif and OaA3Z2-Z3 have yet to be elucidated. Here, we identified the cellular factors ElonginB/C, CYPA and Cullin5 as being hijacked by CAEV Vif as well as several functional domains of CAEV Vif requ
Thu Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2020
Sensing and Transmitting Intracellular Amino Acid Signals through Reversible Lysine Aminoacylations.
Cell metabolism
He XD,Gong W,Zhang JN,Nie J,Yao CF,Guo FS,Lin Y,Wu XH,Li F,Li J,Sun WC,Wang ED,An YP,Tang HR,Yan GQ,Yang PY,Wei Y,Mao YZ,Lin PC,Zhao JY,Xu Y,Xu W,Zhao SM
Amino acids are known regulators of cellular signaling and physiology but how they are sensed intracellularly is not fully understood. Herein we report that each aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) senses its cognate amino acid sufficiency through catalyzing the formation of lysine aminoacylation (K-AA) on its specific substrate proteins. At physiologic levels amino acids promote ARSs bound to their substrates and form K-AAs on the ?-amine of lysines in their substrates by producing reactive aminoac
Tue Jan 09 00:00:00 EST 2018
De novo variants in GABRA2 and GABRA5 alter receptor function and contribute to early-onset epilepsy.
Brain : a journal of neurology
Butler KM,Moody OA,Schuler E,Coryell J,Alexander JJ,Jenkins A,Escayg A
GABAA receptors are ligand-gated anion channels that are important regulators of neuronal inhibition. Mutations in several genes encoding receptor subunits have been identified in patients with various types of epilepsy ranging from mild febrile seizures to severe epileptic encephalopathy. Using whole-genome sequencing we identified a novel de novo missense variant in GABRA5 (c.880G > C p.V294L) in a patient with severe early-onset epilepsy and developmental delay. Targeted resequencing of 279 a
Wed Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
The InR/Akt/TORC1 Growth-Promoting Signaling Negatively Regulates JAK/STAT Activity and Migratory Cell Fate during Morphogenesis.
Developmental cell
Kang D,Wang D,Xu J,Quan C,Guo X,Wang H,Luo J,Yang Z,Chen S,Chen J
Cell growth and cell differentiation are two distinct yet coupled developmental processes, but how they are coordinated is not well understood. During Drosophila oogenesis, we found that the growth-promoting InR/Akt/TOR pathway was involved in suppressing the fate determination of the migratory border cells. The InR/Akt/TOR pathway signals through TOR and Raptor, components of TORC1, to downregulate the JAK/STAT pathway, which is necessary and sufficient for border cell fate determinat
Mon Feb 26 00:00:00 EST 2018
Cecal Ligation and Puncture Alters Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression.
Critical care medicine
Abraham MN,Jimenez DM,Fernandes TD,Deutschman CS
Interventional trials on glucocorticoids in sepsis have yielded capricious results. Recent studies have identified multiple glucocorticoid receptor isoforms. The relative abundance of these isoforms in septic patients and following murine cecal ligation and puncture is unknown. The objective of this study is to determine the effects of cecal ligation and puncture on glucocorticoid receptor isoform abundance.
Wed Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
Genome-wide analysis of endogenously expressed ZEB2 binding sites reveals inverse correlations between ZEB2 and GalNAc-transferase GALNT3 in human tumors.
Cellular oncology (Dordrecht)
Balcik-Ercin P,Cetin M,Yalim-Camci I,Odabas G,Tokay N,Sayan AE,Yagci T
ZEB2 is a transcriptional repressor that regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through binding to bipartite E-box motifs in gene regulatory regions. Despite the abundant presence of E-boxes within the human genome and the multiplicity of pathophysiological processes regulated during ZEB2-induced EMT only a small fraction of ZEB2 targets has been identified so far. Hence we explored genome-wide ZEB2 binding by chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing (ChIP-seq) under endogenous ZEB
Wed Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
Simulated photoperiod influences testicular activity in quail via modulating local GnRHR-GnIHR, GH-R, Cnx-43 and 14-3-3.
Journal of photochemistry and photobiology. B, Biology
Banerjee S,Chaturvedi CM
The hypothalamo-hypophyseal-gonadal axis mediated differential photosexual responses in quail kept under different simulated photoperiodic conditions have been studied in details. Local testicular GnRH-GnIH and their receptor system has been hypothesized to be modulated in quail showing different photo-sexual responses and thus influence the testicular activity and steroidogenesis through local (paracrine and autocrine) action. To validate this hypothesis, we studied the expression of gonadotrop
Mon Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2018
HIV antiretroviral therapy drugs induce premature senescence and altered physiology in HUVECs.
Mechanisms of ageing and development
Cohen J,D'Agostino L,Tuzer F,Torres C
Developments in medicine have led to a significant increase in the average human lifespan. This increase in aging is most readily apparent in the case of HIV where antiretroviral therapy has shifted infection from a terminal to a chronic but manageable disease. Despite this advance patients suffer from co-morbidities best described as an accelerated aging phenotype. A potential contributor is cellular senescence an aging-associated growth arrest which has already been linked to other HIV co-morb
Mon Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
Protective effects of Progranulin against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress and NF-κB activation in reactive astrocytes.
Journal of cellular biochemistry
Shu Q,Fan H,Li SJ,Zhou D,Ma W,Zhao XY,Yan JQ,Wu G
The aim of this study is to explore the effect progranulin (PGRN) has on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the NF-κB activation in reactive astrocytes found in rat models with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were grouped into the sham, I/R, PGRN-high dose, PGRN-low dose, and negative control (NC) groups. TTC staining was applied in order to detect the cerebral infarction volume, a TUNEL assay to detect the apoptosis rate of neurons, an ELISA t
Wed Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
X-ray irradiation induces disruption of the blood-brain barrier with localized changes in claudin-5 and activation of microglia in the mouse brain.
Neurochemistry international
Yoshida Y,Sejimo Y,Kurachi M,Ishizaki Y,Nakano T,Takahashi A
X-ray irradiation (X-irradiation) induces disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). However the mechanisms underlying the permeability changes are unclear. Therefore in the present study we examined the cellular and molecular changes produced by X-irradiation of the brain. Male ICR mice were irradiated locally on their head posterior to the bregma except for the eyes with a single dose of 60 Gy. BBB permeability was assessed using Evans blue dye. We also examined vascular endothelial growth f
Mon Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2018
A frame-shift deletion in the PURA gene associates with a new clinical finding: Hypoglycorrhachia. Is GLUT1 a new PURA target?
Molecular genetics and metabolism
Mayorga L,Gamboni B,Mampel A,Roqué M
PURA is a DNA/RNA-binding protein known to have an important role as a transcriptional and translational regulator. Mutations in the PURA gene have been documented to cause mainly a neurologic phenotype including hypotonia epilepsy development delay and respiratory alterations. We report here a patient with a frame-shift deletion in the PURA gene that apart from the classical PURA deficiency phenotype had marked hypoglycorrhachia overlapping the clinical findings with a GLUT1 deficiency syndrome
Thu Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2018
SOX7 Suppresses Wnt Signaling by Disrupting β-Catenin/BCL9 Interaction.
DNA and cell biology
Fan R,He H,Yao W,Zhu Y,Zhou X,Gui M,Lu J,Xi H,Deng Z,Fan M
The Wnt signaling is involved in angiogenesis and tumor development. β-catenin is the core component of the Wnt pathway, which mediates oncogenic transcription and regulated by a series of proteins. Sex-determining region Y-box 7 (SOX7) is a member of high-mobility-group transcription factor family, which inhibits oncogenic Wnt signaling in lots of tumor cells with unknown mechanism. By coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) and super Topflash reporter assay, SOX7 can bind β-catenin and inhibit
Thu Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2018
From the Cover: 2.45-GHz Microwave Radiation Impairs Hippocampal Learning and Spatial Memory: Involvement of Local Stress Mechanism-Induced Suppression of iGluR/ERK/CREB Signaling.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology
Shahin S,Banerjee S,Swarup V,Singh SP,Chaturvedi CM
Microwave (MW) radiation induced oxidative stress reduces dendritic arborization spine density and number of hippocampal pyramidal neurons and hence impair learning and spatial memory through p53-dependent/independent apoptosis of hippocampal neuronal and nonneuronal cells. However the mechanisms responsible for MW radiation induced impairment in memory formation remains still unknown. This study elucidates the effect of short (15 days) and long-term (30 and 60 days) low level 2.45 GHz MW radiat
Thu Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2018
Plasmodium falciparum RUVBL3 protein: a novel DNA modifying enzyme and an interacting partner of essential HAT protein MYST.
Scientific reports
Sen U,Saxena H,Khurana J,Nayak A,Gupta A
RUVBLs constitute a conserved group of ATPase proteins that play significant role in a variety of cellular processes including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle and DNA damage repair. Three RUVBL homologues, namely, PfRUVBL1, PfRUVBL2 and PfRUVBL3 have been identified in P. falciparum, unlike its eukaryotic counterparts, which have two RUVBL proteins (RUVBL1 & RUVBL2). The present study expands our understanding of PfRUVBL3 protein and thereby basic biology of Plasmodium in general. Here, w
Thu Jul 19 00:00:00 EDT 2018
Colonic Lysine Homocysteinylation Induced by High-Fat Diet Suppresses DNA Damage Repair.
Cell reports
Wang D,Zhao R,Qu YY,Mei XY,Zhang X,Zhou Q,Li Y,Yang SB,Zuo ZG,Chen YM,Lin Y,Xu W,Chen C,Zhao SM,Zhao JY
Colorectal cancer (CRC) onset is profoundly affected by Western diet. Here, we report that high-fat (HF) diet-induced, organ-specific colonic lysine homocysteinylation (K-Hcy) increase might promote CRC onset by impeding DNA damage repair. HF chow induced elevated methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MARS) expression and K-Hcy levels and DNA damage accumulation in the mouse and rat colon, resulting in a phenotype identical to that of CRC tissues. Moreover, the increased copy number of MARS, whose pro
Tue Oct 09 00:00:00 EDT 2018
Inhibition of NF-κB by Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Prevents the Inflammatory Response in a Ligature-Induced Peri-Implantitis Model: A Canine Study.
Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology
He CY,Jiang LP,Wang CY,Zhang Y
The roles of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in peri-implantitis are unclear. Here we used a canine model of peri-implantitis to explore the effects of inhibiting NF-κB with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) on the inflammatory response in ligature-induced peri-implantitis.
Tue Sep 18 00:00:00 EDT 2018
CLOCK Acetylates ASS1 to Drive Circadian Rhythm of Ureagenesis.
Molecular cell
Lin R,Mo Y,Zha H,Qu Z,Xie P,Zhu ZJ,Xu Y,Xiong Y,Guan KL
In addition to responding to environmental entrainment with diurnal variation metabolism is also tightly controlled by cell-autonomous circadian clock. Extensive studies have revealed key roles of transcription in circadian control. Post-transcriptional regulation for the rhythmic gating of metabolic enzymes remains elusive. Here we show that arginine biosynthesis and subsequent ureagenesis are collectively regulated by CLOCK (circadian locomotor output cycles kaput) in circadian rhythms. Facili
Thu Oct 05 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Endothelin Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Activating YAP/TAZ.
Cancer research
Wang Z,Liu P,Zhou X,Wang T,Feng X,Sun YP,Xiong Y,Yuan HX,Guan KL
Endothelin receptor A (ETAR) promotes tumorigenesis by stimulating cell proliferation, migration, and survival. However, the mechanism of ETAR in promoting tumor growth is largely unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that ETAR stimulates colon cell proliferation, migration, and tumorigenesis through the activation of YAP/TAZ, two transcription coactivators of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway. Endothelin-1 treatment induced YAP/TAZ dephosphorylation, nuclear accumulation, and transcriptional
Mon May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Complement modulation in the retinal pigment epithelium rescues photoreceptor degeneration in a mouse model of Stargardt disease.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Lenis TL,Sarfare S,Jiang Z,Lloyd MB,Bok D,Radu RA
Recessive Stargardt macular degeneration (STGD1) is caused by mutations in the gene for the ABCA4 transporter in photoreceptor outer segments. STGD1 patients and Abca4-/- (STGD1) mice exhibit buildup of bisretinoid-containing lipofuscin pigments in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), increased oxidative stress, augmented complement activation and slow degeneration of photoreceptors. A reduction in complement negative regulatory proteins (CRPs), possibly owing to bisretinoid accumulation, may b
Tue Apr 11 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Coronavirus nonstructural protein 15 mediates evasion of dsRNA sensors and limits apoptosis in macrophages.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Deng X,Hackbart M,Mettelman RC,O'Brien A,Mielech AM,Yi G,Kao CC,Baker SC
Tue May 23 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Critical role of the cAMP-PKA pathway in hyperglycemia-induced epigenetic activation of fibrogenic program in the kidney.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
Deb DK,Bao R,Li YC
Hyperglycemia is a major pathogenic factor that promotes diabetic nephropathy, but the underlying mechanism remains incompletely understood. Here, we show that high glucose induced cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP)-mediated H3K9/14 hyperacetylation in approximately 5000 gene promoters in glomerular mesangial cells, including those of Tgfb1, Tgfb3, and Ctgf, the major profibrotic factors that are known to drive diabetic renal fibrogenesis. In these promoters, H3K9
Mon May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Astrocyte Senescence and Metabolic Changes in Response to HIV Antiretroviral Therapy Drugs.
Frontiers in aging neuroscience
Cohen J,D'Agostino L,Wilson J,Tuzer F,Torres C
With the advent of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) survival rates among patients infected by HIV have increased. However even though survival has increased HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) still persist suggesting that HAART-drugs may play a role in the neurocognitive impairment observed in HIV-infected patients. Given previous data demonstrating that astrocyte senescence plays a role in neurocognitive disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) we examined the role of
Sat Sep 25 00:00:00 EDT 2021
Endoplasmic reticulum protein ERp46 in prostate adenocarcinoma.
Oncology letters
Duivenvoorden WCM,Hopmans SN,Austin RC,Pinthus JH
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein ERp46 is a member of the protein disulfide isomerase family of oxidoreductases, which facilitates the reduction of disulfides in proteins and their folding. Accumulation of misfolded proteins has been implicated in cancer. The objectives of the present study were to investigate the role of ERp46 in prostate cancer, its expression and its effects on prostate cancer growth. A tissue microarray with human prostate cancer and normal prostate tissue samples was stai
Mon May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2017
DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects endothelial cells against advanced glycation end product-induced injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation responses.
Experimental and therapeutic medicine
Liu CY,Zhao ZH,Chen ZT,Che CH,Zou ZY,Wu XM,Chen SG,Li YX,Lin HB,Wei XF,You J,Huang HP
Endothelial dysfunction regarded as a key step in the pathophysiological course of diabetic vascular complications is initiated and deteriorated by advanced glycation end products (AGEs). DL-3-n-butylphthalide (DL-NBP) has been proven to have protective effects on neurons and vascular endothelial cells against ischemic and anoxic damage. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether NBP is able to attenuate AGE-induced endothelial dysfunction and also elucidate the possible underlying
Fri Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2017
A simple optogenetic MAPK inhibitor design reveals resonance between transcription-regulating circuitry and temporally-encoded inputs.
Nature communications
Melero-Fernandez de Mera RM,Li LL,Popinigis A,Cisek K,Tuittila M,Yadav L,Serva A,Courtney MJ
Engineering light-sensitive protein regulators has been a tremendous multidisciplinary challenge. Optogenetic regulators of MAPKs central nodes of cellular regulation have not previously been described. Here we present OptoJNKi a light-regulated JNK inhibitor based on the AsLOV2 light-sensor domain using the ubiquitous FMN chromophore. OptoJNKi gene-transfer allows optogenetic applications whereas protein delivery allows optopharmacology. Development of OptoJNKi suggests a design principle for o
Fri May 12 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Enoyl-CoA hydratase-1 regulates mTOR signaling and apoptosis by sensing nutrients.
Nature communications
Zhang YK,Qu YY,Lin Y,Wu XH,Chen HZ,Wang X,Zhou KQ,Wei Y,Guo F,Yao CF,He XD,Liu LX,Yang C,Guan ZY,Wang SD,Zhao J,Liu DP,Zhao SM,Xu W
The oncogenic mechanisms of overnutrition, a confirmed independent cancer risk factor, remain poorly understood. Herein, we report that enoyl-CoA hydratase-1 (ECHS1), the enzyme involved in the oxidation of fatty acids (FAs) and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), senses nutrients and promotes mTOR activation and apoptotic resistance. Nutrients-promoted acetylation of lys101 of ECHS1 impedes ECHS1 activity by impairing enoyl-CoA binding, promoting ECHS1 degradation and blocking its mit
Wed Sep 06 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Combined venetoclax and alvocidib in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget
Bogenberger J,Whatcott C,Hansen N,Delman D,Shi CX,Kim W,Haws H,Soh K,Lee YS,Peterson P,Siddiqui-Jain A,Weitman S,Stewart K,Bearss D,Mesa R,Warner S,Tibes R
More effective treatment options for elderly acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients are needed as only 25-50% of patients respond to standard-of-care therapies response duration is typically short and disease progression is inevitable even with some novel therapies and ongoing clinical trials. Anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family inhibitors such as venetoclax are promising therapies for AML. Nonetheless resistance is emerging. We demonstrate that venetoclax combined with cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhi
Tue Dec 05 00:00:00 EST 2017
RCC1-dependent activation of Ran accelerates cell cycle and DNA repair, inhibiting DNA damage-induced cell senescence.
Molecular biology of the cell
Cekan P,Hasegawa K,Pan Y,Tubman E,Odde D,Chen JQ,Herrmann MA,Kumar S,Kalab P
The coordination of cell cycle progression with the repair of DNA damage supports the genomic integrity of dividing cells. The function of many factors involved in DNA damage response (DDR) and the cell cycle depends on their Ran GTPase-regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic transport (NCT). The loading of Ran with GTP which is mediated by RCC1 the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ran is critical for NCT activity. However the role of RCC1 or Ran⋅GTP in promoting cell proliferation or DDR is no
Fri Apr 15 00:00:00 EDT 2016
Phosphorylation of BMK1 induces prostatic carcinoma cell proliferation by promoting entry into the S phase of the cell cycle.
Oncology letters
Xiong Y,Zhang L,Wang T
Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) is activated by mitogens and oncogenic signals and is strongly implicated in tumorigenesis. In the present study it was demonstrated that the activation of BMK1 but not extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 can induce proliferation in prostate cancer cells. It was found that the proliferation of epidermal growth factor (EGF)-treated cells was accelerated by 40% compared with non-treated cells using a CCK8 assay. In addition cell cycle analys
Fri Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2016
Matrix metalloproteinase 14 participates in corneal lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway.
Experimental and therapeutic medicine
Du HT,Liu P
The aim of the present study was to investigate the roles of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP-14) in corneal inflammatory lymphangiogenesis. The expression of MMP-14 was detected by immunohistochemistry, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and western blot assays, under various corneal conditions. pCMV-MMP-14 or empty pCMV vectors were injected into mouse corneal stroma, 3 days after suture placement in a standard suture-induced inflammatory corneal neovascula
Sat Oct 01 00:00:00 EDT 2016
Sc65-Null Mice Provide Evidence for a Novel Endoplasmic Reticulum Complex Regulating Collagen Lysyl Hydroxylation.
PLoS genetics
Heard ME,Besio R,Weis M,Rai J,Hudson DM,Dimori M,Zimmerman SM,Kamykowski JA,Hogue WR,Swain FL,Burdine MS,Mackintosh SG,Tackett AJ,Suva LJ,Eyre DR,Morello R
Collagen is a major component of the extracellular matrix and its integrity is essential for connective tissue and organ function. The importance of proteins involved in intracellular collagen post-translational modification folding and transport was recently highlighted from studies on recessive forms of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). Here we describe the critical role of SC65 (Synaptonemal Complex 65 P3H4) a leprecan-family member as part of an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) complex with prolyl 3-h
Fri Apr 01 00:00:00 EDT 2016
PERK Regulates Working Memory and Protein Synthesis-Dependent Memory Flexibility.
PloS one
Zhu S,Henninger K,McGrath BC,Cavener DR
PERK (EIF2AK3) is an ER-resident eIF2α kinase required for memory flexibility and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression processes known to be dependent on new protein synthesis. Here we investigated PERK's role in working memory a cognitive ability that is independent of new protein synthesis but instead is dependent on cellular Ca2+ dynamics. We found that working memory is impaired in forebrain-specific Perk knockout and pharmacologically PERK-inhibited mice. Mor
Fri Aug 11 00:00:00 EDT 2017
Proteolytic processing of the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis related lysosomal protein CLN5.
Experimental cell research
De Silva B,Adams J,Lee SY
CLN5 is a soluble lysosomal glycoprotein. Deficiency in CLN5 protein causes neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, an inherited neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorder. The function of CLN5 and how it affects lysosome activity are unclear. We identified two forms of the CLN5 protein present in most of the cell lines studied. The molecular mass difference between these two forms is about 4kDa. The fibroblast cells derived from two CLN5 patients lack both forms. Using transient transfection, we show
Thu Oct 15 00:00:00 EDT 2015
Ubiquitin E3 Ligase LNX2 is Critical for Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro by Regulating M-CSF/RANKL Signaling and Notch2.
Calcified tissue international
Zhou J,Fujiwara T,Ye S,Li X,Zhao H
The Notch signaling pathway plays a crucial role in skeletal development and homeostasis by regulating the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. However, the molecular mechanisms modulating the level and activity of Notch receptors in bone cells remain unknown. In this study, we uncovered that LNX2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase and Notch inhibitor Numb binding protein, was up-regulated during osteoclast differentiation. Knocking-down LNX2 expression in bone marrow macrophag
Fri May 01 00:00:00 EDT 2015
Nesfatin-1: Localization and expression in avian gonads and its modulation by temporal phase relation of neural oscillations in female Japanese quail, Coturnix coturnix japonica.
General and comparative endocrinology
Banerjee S,Chaturvedi CM
In a search for new appetite-controlling signals, the peptide nesfatin-1, expressed in the brain and peripheral tissues of rodents and humans has been reported to regulate feeding by reducing food intake. Recently it has also been reported that nesfatin-1 might be involved in regulating the reproductive axis in fishes and mammals, but its expression and physiological role if any, is not yet known in birds. In the present study, localization and expression of nesfatin-1 was observed in the testis
Tue Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2015
COPS5 protein overexpression increases amyloid plaque burden, decreases spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta, and exacerbates learning and memory deficits in the mouse brain.
The Journal of biological chemistry
Wang R,Wang H,Carrera I,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
Brain accumulation of neurotoxic amyloid β (Aβ) peptide because of increased processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) resulting in loss of synapses and neurodegeneration is central to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD). Therefore the identification of molecules that regulate Aβ generation and those that cause synaptic damage is crucial for future therapeutic approaches for AD. We demonstrated previously that COPS5 regulates Aβ generation in neuronal cell lines in
Fri Apr 03 00:00:00 EDT 2015
Coupled local translation and degradation regulate growth cone collapse.
Nature communications
Deglincerti A,Liu Y,Colak D,Hengst U,Xu G,Jaffrey SR
Local translation mediates axonal responses to Semaphorin3A (Sema3A) and other guidance cues. However, only a subset of the axonal proteome is locally synthesized, whereas most proteins are trafficked from the soma. The reason why only specific proteins are locally synthesized is unknown. Here we show that local protein synthesis and degradation are linked events in growth cones. We find that growth cones exhibit high levels of ubiquitination and that local signalling pathways trigger the ubiqui
Wed Apr 22 00:00:00 EDT 2015
Stability of HIB-Cul3 E3 ligase adaptor HIB Is Regulated by Self-degradation and Availability of Its Substrates.
Scientific reports
Zhou Z,Xu C,Chen P,Liu C,Pang S,Yao X,Zhang Q
The HIB-Cul3 complex E3 ligase regulates physiological homeostasis through regulating its substrate stability and its activity can be modulated by changing HIB abundance. However, regulation of HIB remains elusive. Here we provide evidence that HIB is degraded through the proteasome by Cul3-mediated polyubiquitination in K48 manner in Drosophila. Strikingly, HIB is targeted for degradation by itself. We further identify that three degrons ((52)LKSS(56)T, (76)LDEE(80)S and (117)MESQ(121)R) and K1
Wed Aug 12 00:00:00 EDT 2015
The same site on the integrase-binding domain of lens epithelium-derived growth factor is a therapeutic target for MLL leukemia and HIV.
Blood
Murai MJ,Pollock J,He S,Miao H,Purohit T,Yokom A,Hess JL,Muntean AG,Grembecka J,Cierpicki T
Lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) is a chromatin-associated protein implicated in leukemia and HIV type 1 infection. LEDGF associates with mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) fusion proteins and menin and is required for leukemic transformation. To better understand the molecular mechanism underlying the LEDGF integrase-binding domain (IBD) interaction with MLL fusion proteins in leukemia we determined the solution structure of the MLL-IBD complex. We found a novel MLL motif integrase domai
Thu Dec 11 00:00:00 EST 2014
High expression of beta2-glycoprotein I is associated significantly with the earliest stages of hepatitis B virus infection.
Journal of medical virology
Liu YM,Zhang WY,Wang ZF,Yan CY,Gao PJ
Human beta2-glycoprotein I (beta2-GPI) binds to recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen (rHBsAg) and can bind specifically to annexin II, which is located on the cell membrane of human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Viral envelope proteins are essential for mediating cellular entry. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of beta2-GPI in the early stages of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Western blot and qRT-PCR analyses revealed that beta2-GPI expression was upregulated in HepG2.2.15 c
Fri Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2014
NOTCH-induced aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 deacetylation promotes breast cancer stem cells.
The Journal of clinical investigation
Zhao D,Mo Y,Li MT,Zou SW,Cheng ZL,Sun YP,Xiong Y,Guan KL,Lei QY
High aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity is a marker commonly used to isolate stem cells, particularly breast cancer stem cells (CSCs). Here, we determined that ALDH1A1 activity is inhibited by acetylation of lysine 353 (K353) and that acetyltransferase P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) and deacetylase sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) are responsible for regulating the acetylation state of ALDH1A1 K353. Evaluation of breast carcinoma tissues from patients revealed that cells with high ALDH1 activity have lo
Mon Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2014
RanBP9 overexpression accelerates loss of dendritic spines in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiology of disease
Wang R,Palavicini JP,Wang H,Maiti P,Bianchi E,Xu S,Lloyd BN,Dawson-Scully K,Kang DE,Lakshmana MK
We previously demonstrated that RanBP9 overexpression increased Aβ generation and amyloid plaque burden, subsequently leading to robust reductions in the levels of several synaptic proteins as well as deficits in the learning and memory skills in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the present study, we found striking reduction of spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta (52%, p<0.001) and spinophilin area (62.5%, p<0.001) in the primary cortical neurons derived from RanBP9 tr
Mon Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2014
Sc65 is a novel endoplasmic reticulum protein that regulates bone mass homeostasis.
Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research
Gruenwald K,Castagnola P,Besio R,Dimori M,Chen Y,Akel NS,Swain FL,Skinner RA,Eyre DR,Gaddy D,Suva LJ,Morello R
Members of the Leprecan family of proteins include enzymes, prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 (P3h1), P3h2 and P3h3, and non-enzymatic proteins, Crtap and Sc65. Mutations in CRTAP and LEPRE1 (encoding P3H1) have been associated with human disease such as recessive osteogenesis imperfecta, however, the function of Sc65 which is closely related and highly homologous to Crtap is unknown. Sc65 has been described as a synaptonemal complex protein, a nucleolar protein, and a cytoplasmic adapter protein. In light
Sat Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2014
RACK-1 regulates let-7 microRNA expression and terminal cell differentiation in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
Chu YD,Wang WC,Chen SA,Hsu YT,Yeh MW,Slack FJ,Chan SP
The let-7 microRNA (miRNA) regulates cell cycle exit and terminal differentiation in the C. elegans heterochronic gene pathway. Low expression of let-7 results in retarded vulva and hypodermal cell development in C. elegans and has been associated with several human cancers. Previously, the versatile scaffold protein receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) was proposed to facilitate recruitment of the miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) to the polysome and to be required for miRNA functio
Tue Jan 20 00:00:00 EST 2015
RanBP9 overexpression down-regulates phospho-cofilin, causes early synaptic deficits and impaired learning, and accelerates accumulation of amyloid plaques in the mouse brain.
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD
Palavicini JP,Wang H,Minond D,Bianchi E,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
Loss of synaptic proteins and functional synapses in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) as well as transgenic mouse models expressing amyloid-β protein precursor is now well established. However, the earliest age at which such loss of synapses occurs, and whether known markers of AD progression accelerate functional deficits is completely unknown. We previously showed that RanBP9 overexpression leads to enhanced amyloid plaque burden in a mouse model of AD. In this st
Thu Oct 30 00:00:00 EDT 2014
RanBP9 overexpression reduces dendritic arbor and spine density.
Neuroscience
Wang H,Lewsadder M,Dorn E,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
RanBP9 is a multi-domain scaffolding protein known to integrate extracellular signaling with intracellular targets. We previously demonstrated that RanBP9 enhances Aβ generation and amyloid plaque burden which results in loss of specific pre- and postsynaptic proteins in vivo in a transgenic mouse model. Additionally, we showed that the levels of spinophilin, a marker of dendritic spines were inversely proportional to the RanBP9 protein levels within the synaptosomes isolated from AD brains
Fri Apr 18 00:00:00 EDT 2014
Modulation of hepatitis B surface antigen secretion by annexin II expressed in hepatitis B virus‑producing hepatoma cells.
Molecular medicine reports
Liu Y,Gao P
The role of annexin II in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains to be elucidated. Intracellular hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-retention contributes to the induction of hepatocarcinogenesis. The present study aimed to investigate the regulation of HBsAg secretion by annexin II expressed in HBV-producing hepatoma cells. The expression of annexin II was analyzed using western blot analysis in SMMC-7721, HepG2, HepG2.2.15, 293T and Chinese hamster ovary (CHO
Mon Dec 01 00:00:00 EST 2014
RanBP9 overexpression accelerates loss of pre and postsynaptic proteins in the APΔE9 transgenic mouse brain.
PloS one
Wang H,Wang R,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
[This corrects the article DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085484.].
Wed Sep 17 00:00:00 EDT 2014
COPS5 (Jab1) protein increases β site processing of amyloid precursor protein and amyloid β peptide generation by stabilizing RanBP9 protein levels.
The Journal of biological chemistry
Wang H,Dey D,Carrera I,Minond D,Bianchi E,Xu S,Lakshmana MK
Increased processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and accumulation of neurotoxic amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) in the brain is central to the pathogenesis of Alzheimers disease (AD). Therefore identification of molecules that regulate Aβ generation is crucial for future therapeutic approaches for AD. We previously demonstrated that RanBP9 regulates Aβ generation in a number of cell lines and primary neuronal cultures, by forming tripartite protein complexes with APP, LRP and B
Fri Sep 13 00:00:00 EDT 2013
Striking reduction of amyloid plaque burden in an Alzheimer's mouse model after chronic administration of carmustine.
BMC medicine
Hayes CD,Dey D,Palavicini JP,Wang H,Patkar KA,Minond D,Nefzi A,Lakshmana MK
BACKGROUND: Currently available therapies for Alzheimer's disease (AD) do not treat the underlying cause of AD. Anecdotal observations in nursing homes from multiple studies strongly suggest an inverse relationship between cancer and AD. Therefore, we reasoned that oncology drugs may be effective against AD. METHODS: We screened a library of all the FDA-approved oncology drugs and identified bis-chloroethylnitrosourea (BCNU or carmustine) as an effective amyloid beta (Aβ) reducing comp
Tue Mar 26 00:00:00 EDT 2013
RanBP9 aggravates synaptic damage in the mouse brain and is inversely correlated to spinophilin levels in Alzheimer's brain synaptosomes.
Cell death & disease
Palavicini JP,Wang H,Bianchi E,Xu S,Rao JS,Kang DE,Lakshmana MK
We previously demonstrated that overexpression of RanBP9 led to enhanced A? generation in a variety of cell lines and primary neuronal cultures, and subsequently, we confirmed increased amyloid plaque burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the present study, we found striking reduction of spinophilin protein levels when RanBP9 is overexpressed. At 12 months of age, we found spinophilin levels reduced by 70% (P<0.001) in the cortex of AP?E9/RanBP9 mice compared with that in wild-
Thu Jun 13 00:00:00 EDT 2013
BACE1 elevation is involved in amyloid plaque development in the triple transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease: differential Aβ antibody labeling of early-onset axon terminal pathology.
Neurotoxicity research
Cai Y,Zhang XM,Macklin LN,Cai H,Luo XG,Oddo S,Laferla FM,Struble RG,Rose GM,Patrylo PR,Yan XX
β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilins mutations cause early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). Some FAD-based mouse models produce amyloid plaques, others do not. β-Amyloid (Aβ) deposition can manifest as compact and diffuse plaques; it is unclear why the same Aβ molecules aggregate in different patterns. Is there a basic cellular process governing Aβ plaque pathogenesis? We showed in some FAD mouse models that compact plaque formation is associat
Wed Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2012
Chronic cladribine administration increases amyloid beta peptide generation and plaque burden in mice.
PloS one
Hayes CD,Dey D,Palavicini JP,Wang H,Araki W,Lakshmana MK
BACKGROUND: The clinical uses of 2-chloro-2'-deoxyadenosine (2-CDA) or cladribine which was initially prescribed to patients with hematological and lymphoid cancers is now extended to treat patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Previous data has shown that 2-CDA has high affinity to the brain and readily passes through the blood brain barrier reaching CSF concentrations 25% of that found in plasma. However, whether long-term administration of 2-CDA can lead to any adverse effects in patien
Tue Apr 02 00:00:00 EDT 2013