Search Thermo Fisher Scientific

High-throughput, high-parameter cell sorting with integrated biocontainment
The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter integrates advanced fluorescence-activated cell sorting technology that enables simple operation and a wide range of cell sorting applications. It combines performance, safety, and ease-of-use to fit seamlessly into the workflow of both individual labs and core facilities. The Bigfoot is capable of spectral unmixing or conventional compensation for high-parameter, high-throughput cell sorting experiments and maximum flexibility.
Streamlined design
Designed for today’s cell sorting applications from simple to complex, the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter is loaded with thoughtful design features that help increase flexibility, boost performance, and streamline your workflow. For example, calibration beads are kept ready for use onboard the sample loader, eliminating the need to prepare a new calibration solution each day. (Simply replace the spent vial with a new one about once a month.) Within the biocontainment field there is ample deck space for sample racks and plates as well as access to a built-in sample vortex mixer, tube rack, and biohazard bag. This allows the operator to complete many routine tasks without breaching the safety barrier.

With multiple cameras and sensors throughout, the system monitors system health, provides feedback on all subsystems, and logs status for proactive troubleshooting. Built-in bubble detection automatically stops sampling and notifies the operator when the sample tube is nearly empty, reducing dead volume. The system tracks the volume of sorted samples and can change collection tubes automatically when full.
Exceptionally fast high-throughput cell sorting
The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter is capable of sorting up to 70,000* events per second (eps) and analysis rates of more than 100,000 eps. It is also capable of 6-way sorting into tubes, four-way sorting into 96-well and 384-well plates, or straight-down sorting into 1536-well plates. The Bigfoot Cell Sorter can sort a 96-well plate in as little as 8 seconds, and a 384-well plate in as little as 20 seconds. In addition, virtual 18-way sorting allows researchers to separate multiple populations from a single sample or different samples in sets of 6 populations. For high throughput micro-titer plate sorts, the InfiniSort capability lets you perform multiple plate sorts in fast sequence.
*actual sort rates depend on application
The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter offers robust and high-performance plate sorting capabilities, providing consistent deposition efficiency and cell recovery for optimal input into downstream experiments. Using the HRP method, with visual confirmation of droplet deposition through the colorimetric conversion of TMB substrate, we have shown that a single droplet can be sorted in small volumes into both 96-well and 384-well PCR plates with 100% targeting accuracy. Our white paper explains the engineering innovations we have developed to obtain such fast and accurate sorting.
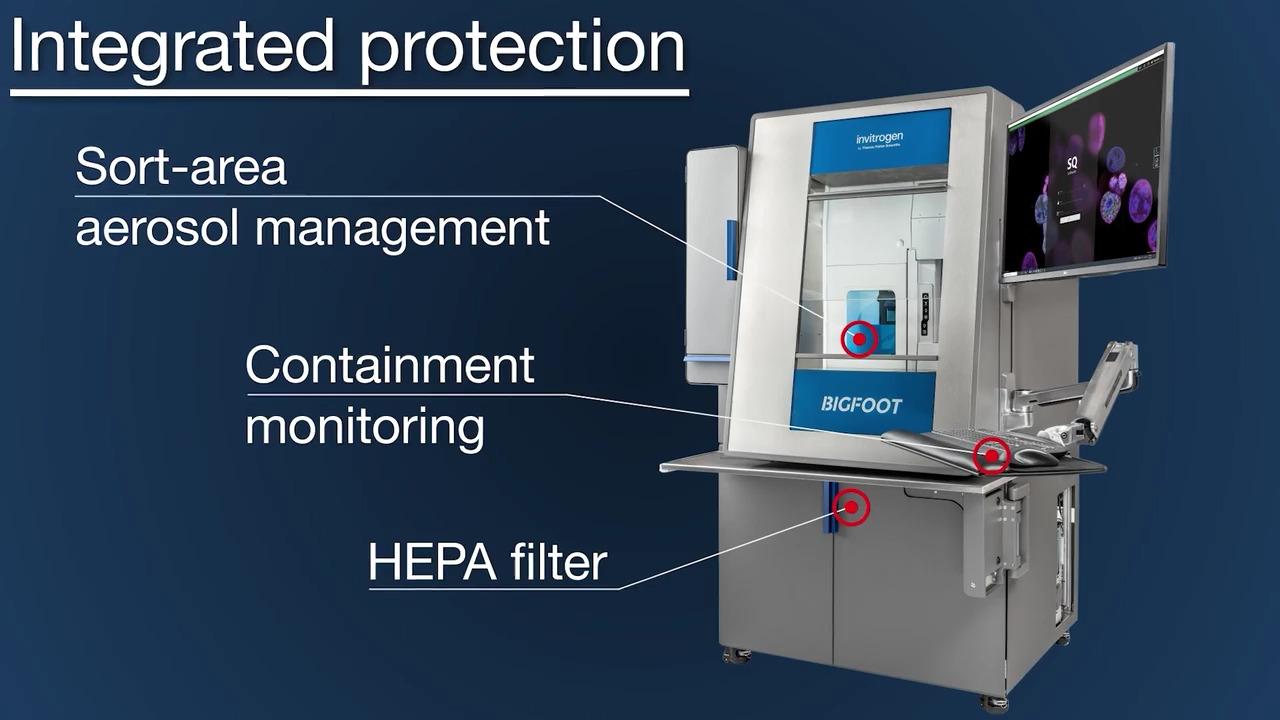
Integrated biocontainment and aerosol management
The Bigfoot Cell Sorter features an integrated biocontainment enclosure which provides personnel and product protection similar to a Class II biosafety cabinet.
Test procedures and criteria laid out within NSF49 and EN12469 can be utilized to demonstrate performance. The custom designed enclosure and aerosol management system (AMS) protects operators and samples from aerosols without compromising high-parameter sorter performance or impacting workflow while complying with ISAC biosafety guidelines.
Thoughtful design has converted biocontainment from a cumbersome add-on to an integrated part of the Bigfoot instrument and user workflows. The adjustable sash can easily be raised or lowered for safe access to the sample area or sorting nozzles. An internal control panel in the sample area limits the need for the operator to reach in and out of the containment field. HEPA filtered air flowing through the cabinet is exhausted either into the laboratory or via an optional canopy connection, through an external exhaust system.
Conventional compensation or spectral unmixing
All Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter configurations enable traditional compensation methods to account for spillover from one fluorophore (color) into another fluorophore’s detector. The Sasquatch (SQ) software builds and applies up to a 60 x 60 compensation matrix (using all 60 detectors) for high-color experiments. This makes migrating your existing conventional flow cytometry experiments to your Bigfoot instrument easy, without the need to change protocols or analysis methods.
In addition, most Bigfoot configurations have spectral flow cytometry capability, allowing for either spectral unmixing or traditional compensation to separate the signals from different fluorophores. By analyzing the full emission spectrum from every fluorophore in your experiment, spectral unmixing allows you to use fluorophores with similar emission profiles to enable a higher number of parameters in your experiment with an easier, more reproducible workflow. This is especially useful for deep immunophenotyping and biomarker screening.
With Bigfoot spectral configurations, you can run both conventional and spectral experiments on the same sorter and convert experiments from traditional compensation to spectral when you need more parameters.
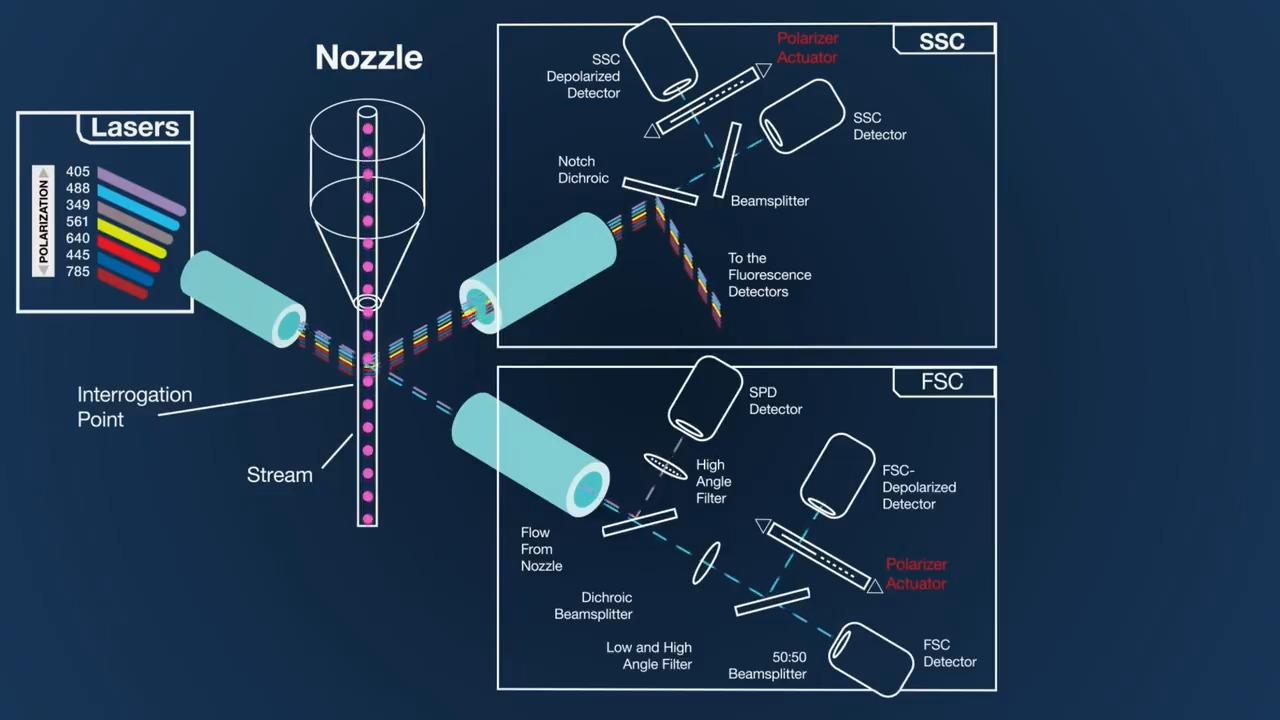
Spectral flow cytometry
One important benefit of spectral unmixing and analysis is a dramatic increase in the number of parameters (fluorophores) that can be detected in a single experiment. The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter can be configured with up to 9 lasers** and 60 detectors, supporting spectral sorting and analysis of cell populations in expansive panels, such as those used for deep immunophenotyping. For example, the figure below shows a combined spectral signature graph for multiple fluorophores, showing not only how each fluorophore’s signature is unique, but also where additional fluorophores might be added.
**The following lasers are used for spectral unmixing: 349nm, 405nm, 445nm, 488nm, 561nm, 640nm, 785nm
A second advantage of spectral unmixing and analysis is that autofluorescence can be treated as just another fluorophore with its own spectral signature. Unlike in conventional flow cytometry, autofluorescence does not limit dye options and can be assessed or eliminated depending on the needs of the experiment.
For a detailed examination of spectral flow cytometry hardware, optics, analysis, advantages, and disadvantages, see the article Spectral Flow Cytometry Fundamentals in our Flow Cytometry Learning Center.
Real-time spectral unmixing
Some spectral cell analyzers perform unmixing after all cells are acquired, but this is inadequate for cell sorting, since cells are sorted as they are acquired and processed. The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter performs unmixing in real time and applies the results to the sort. A massively parallel, pipelined data processing architecture eliminates hard aborts that can result in lost events with higher event rates. The high resolution of the unmixing algorithm allows accurate setting of sort gates maintaining the purity of the sorted cell populations.
Spectral sorting applications
The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter is especially well suited for sorting applications that require high parameter panels and high throughput.
Immunology
Immunophenotyping parameters have increased as researchers study cell subsets beyond major immune subgroups such as effector and memory cells.
Cell and gene therapy research
Therapeutic candidates such as stem cells and CAR-T cells must be efficiently sorted both pre- and post-manipulation.
Gene editing
Sort cells of interest prior to gene editing and collect populations of cells edited by CRISPR or other methods.
Gene sequencing
With output flexibility, the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter can sort single cells directly onto a 10X Genomics chip.
Automation and wizard-driven software
Advanced automation and software wizards allow operators with all levels of knowledge to use and control the system with confidence. For example, the formation and timing of cell-containing droplets—the drop delay between interrogation of the cell and its break-off from the stream—is crucial to help ensure that the correct cells are sorted into the correct tubes. Integrated control systems automatically enable optimal droplet formation persistence and position stabilization over time, calculating and maintaining accurate and stable drop delay through the day.
Automated stream calibration, quality control, and drop delay streamline workflow and reduce user errors. Semi-automated startup lets you program the system to be ready when you are. The electronics automatically configure optimal laser delay for different nozzle sizes and pressures. If a bubble is detected, the system notifies the operator and stops the sort to preserve precious samples. Integrated sample temperature control (from 4–37°C) and agitation maintain the integrity of sample input, while output temperature control (also from 4–37°C) maintains the viability of sorted samples.
Sasquatch (SQ) software presents a clean user interface with intuitive workflow, simplifying acquisition, analysis, and sorting. An advanced fluorophore selector helps with panel design for both standard and spectral experiments and warns of potential fluorophore conflicts. The experiment wizard assists in running controls, identifying potential issues, and applying the unmixing algorithms.
Analysis features include overlays, color-gating, back-gating, index sorting, and ratio plots. The software generates FCS (flow cytometry standard) files compatible with other analysis software packages and produces clear reports on system usage, quality control, trends, and a sort summary.
Flexible cell sorting system supports a broad range of cell types
The Bigfoot system offers sampling from six input positions that automatically detect the tube size (1.5, 5, or 15 mL) based on the adapter used and includes integrated agitation and temperature control. The multi-sample loader allows the controls for a 5- to 10-color experiment to be loaded in just one or two sets. The multi-tube loading capability is especially efficient for studying 20 or more fluorescence parameters, which is increasingly common in flow cytometry. All sample-related subsystems, including the multi-sample loader, are contained inside the fully integrated biosafety enclosure for optimal safety, efficiency, and performance.
One sample input location is reserved for calibration beads, eliminating the need to retrieve beads from a refrigerator, dilute, and prepare a tube for daily setup. An onboard wash station performs a complete wash and backflush cycle in 8 seconds, resulting in extremely low carryover between samples. When a sample’s volume runs low, the end-of-sample bubble detector responds within 50 ms to stop sampling, wash the probe, and move to the next tube without user interaction.
On the sort output side, the Bigfoot Cell Sorter’s jet-in-air sensing is gentle with fragile cells to maximize viability at high sort speeds without reducing yield. Precise single-droplet targeting ensures unprecedented accuracy, recovery, and speed down to single-cell sorting. Configurable sort output holders include 1.5, 5, 15, and 50 mL tubes, microwell plates up to 1,536 wells, microscope slides, and 10x Genomics chips. A swap tip wizard simplifies setup of 70, 100, 120, and 150 μm nozzle tips.
Lab and core facility friendly
While the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter is designed to fit the workflow of an individual laboratory, it is also well suited as a cell sorting workhorse in a flow cytometry core facility.
You don’t have to take our word for it. In this video, three core facility managers who participated in our beta test program discussed their experiences bringing the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter into their labs. They shared their insights about how the Bigfoot system has earned a place among the cell sorters they manage due to its performance, automation, ease of use, small footprint, low noise level, and flexibility. “I call it the Swiss army knife of cytometers,” said Rachael Walker of the Babraham Institute outside of Cambridge, England.
Although flow cores are increasingly reliant on self-serve instruments, high-end cell sorters have not been easy to convert to end-user operation. “The amount of time and expertise it takes to run [a competitor’s high-end] instrument is beyond the majority of our user base,” said Patricia Rogers of the Broad Institute in Cambridge, MA. “They just don’t have six months to learn how to do laser alignment and verticality like we do.” By incorporating quick startup, automation, software wizards, and easy training, added Rogers, the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter has proved that a high-end sorter can indeed be operated successfully by end users, freeing staff to focus on new technology and assay development.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.