Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
DNA-free DNA Polymerases
Single-use technology in the production of DNA-free PCR enzymes
Thermo Fisher Scientific has developed a manufacturing process using Single Use System (SUS)-based technology with extensive quality control testing to drastically reduce the risk of DNA contaminates in the PCR reagents for commercial supply. The result is the same high level of performance and lot-to-lot consistency that is expected for our standard conventional PCR reagents. These reagents are the perfect choice for PCR assays where higher sensitivity and specificity are needed to minimize ambiguous or false-positive results.
Highlights
- Closed SUS enzyme manufacturing
- Stringent quality control testing
- Adherence to ISO 13485 quality standards
Order enzyme Inquire (bulk size / commercial use) Download poster
Featured video:
DNA-free PCR reagents
Watch how SUS technology minimized the risks of DNA contamination in production of PCR reagents.
White paper: SUS Technology in production of PCR reagents
Download a copy of the white paper to learn how DNA-Free PCR reagents are produced by SUS technology.
DNA-free PCR enzymes advantages
DNA contamination
The manufacturing process for commercially available DNA polymerases typically consists of multiple steps handled by a scientist or operator in an open environment (Figure 1). In addition, one might find that equipment may be shared for the manufacture of other proteins and enzymes. As a result, the purity of a preparation must rely heavily on efficient decontamination steps between processes.
Contaminating DNA commonly found in enzyme preparations can occur during one or all of these many steps throughout the manufacturing process. Not surprisingly, when tested, these DNA polymerases have been shown to contain detectable levels of DNA contaminants [1]. This poses an unacceptable risk for commercial-scale production of DNA polymerase that Thermo Fisher Scientific has addressed with SUS-based manufacturing.

Figure 1. A conventional manufacturing workflow for recombinant enzymes illustrates the risk of DNA contamination. The typical process for enzyme preparation includes repeated opportunities for potential DNA contamination from an open environment to handling by an operator between steps. There is also a potential risk for the carryover of DNA contaminants when utilizing equipment that is shared with other manufacturing processes for the preparation of other enzymes and proteins.
Manufacturing innovation
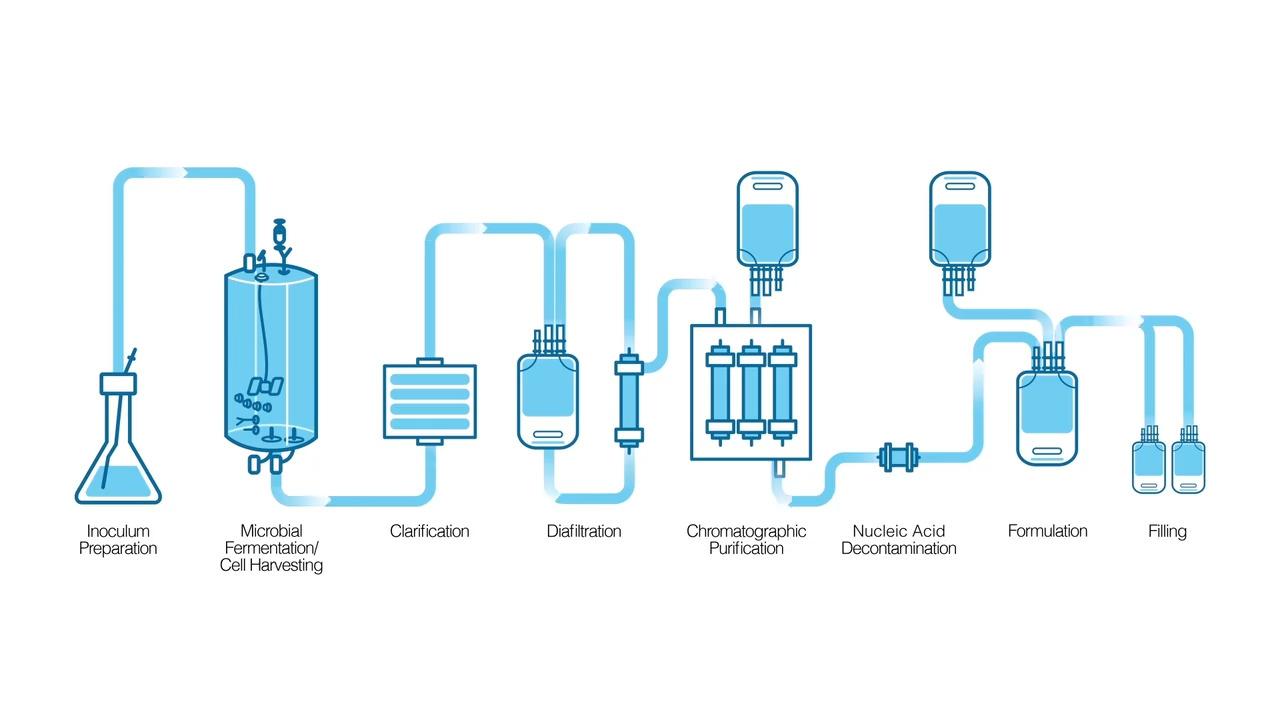
At Thermo Fisher Scientific, we have uniquely adapted our SUS technology for the commercial-scale production of recombinant enzymes (Figure 2). All stages of SUS-based manufacturing are performed within a closed environment and rely on sterile single-use bags, tubing and connectors throughout production. All buffers and washing solutions are prepared in single-use bags and filtered for sterilization. With closed SUS-based manufacturing, the probability of DNA contamination has been reduced to a negligible risk level.
Highlights
- Entirely closed system throughout the manufacturing process–no exposure to environment and human operators
- Sterile single-use bags, tubing and connectors–no potential cross-contamination from common-use equipment
- Manufacturing in facilities that meet Class D and Class C cleanroom standards–dedicated purpose-built space prevents exposure to DNA contaminants

Figure 2. Closed SUS-based process for the manufacture of recombinant enzymes. This process represents a completely closed system that relies on single-use bags, tubes and connectors, which help reduce the potential for DNA contamination to a negligible risk level whether from the environment or the operator. Moreover, because it is single-use and equipment or materials are not shared, it eliminates this as a source of cross-contamination.
Reliable performance
Invitrogen Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, manufactured utilizing the SUS technology, is subjected to rigorous quality control testing (e.g., application-specific functional assays). Real-time PCR assays performed with Platinum Taq DNA polymerase manufactured using SUS technology demonstrates the same performance as compared to Platinum Taq DNA polymerase manufactured using conventional manufacturing scheme.

Figure 3. Sensitive, specific and reproducible amplification with DNA-free Taq DNA polymerase. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (red curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA.
Purity requirement
DNA-Free enzymes are analyzed following the highest standards to ensure the absence of nucleases and DNA contamination per the specifications described below (Table 1).
Table 1. Stringent quality testing to validate DNA-free Platinum Taq DNA polymerase.
| Purity test | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Exonucleases and endonucleases | undetected |
| RNases | undetected |
| Bacterial gDNA (16S rRNA) | ≤0.01 copy/enzyme unit |
| Human gDNA (Alu) | ≤0.001 copy/enzyme unit |
| Plasmid DNA (ori1) | ≤0.01 copy/enzyme unit |
DNA contamination
The manufacturing process for commercially available DNA polymerases typically consists of multiple steps handled by a scientist or operator in an open environment (Figure 1). In addition, one might find that equipment may be shared for the manufacture of other proteins and enzymes. As a result, the purity of a preparation must rely heavily on efficient decontamination steps between processes.
Contaminating DNA commonly found in enzyme preparations can occur during one or all of these many steps throughout the manufacturing process. Not surprisingly, when tested, these DNA polymerases have been shown to contain detectable levels of DNA contaminants [1]. This poses an unacceptable risk for commercial-scale production of DNA polymerase that Thermo Fisher Scientific has addressed with SUS-based manufacturing.

Figure 1. A conventional manufacturing workflow for recombinant enzymes illustrates the risk of DNA contamination. The typical process for enzyme preparation includes repeated opportunities for potential DNA contamination from an open environment to handling by an operator between steps. There is also a potential risk for the carryover of DNA contaminants when utilizing equipment that is shared with other manufacturing processes for the preparation of other enzymes and proteins.
Manufacturing innovation
At Thermo Fisher Scientific, we have uniquely adapted our SUS technology for the commercial-scale production of recombinant enzymes (Figure 2). All stages of SUS-based manufacturing are performed within a closed environment and rely on sterile single-use bags, tubing and connectors throughout production. All buffers and washing solutions are prepared in single-use bags and filtered for sterilization. With closed SUS-based manufacturing, the probability of DNA contamination has been reduced to a negligible risk level.
Highlights
- Entirely closed system throughout the manufacturing process–no exposure to environment and human operators
- Sterile single-use bags, tubing and connectors–no potential cross-contamination from common-use equipment
- Manufacturing in facilities that meet Class D and Class C cleanroom standards–dedicated purpose-built space prevents exposure to DNA contaminants

Figure 2. Closed SUS-based process for the manufacture of recombinant enzymes. This process represents a completely closed system that relies on single-use bags, tubes and connectors, which help reduce the potential for DNA contamination to a negligible risk level whether from the environment or the operator. Moreover, because it is single-use and equipment or materials are not shared, it eliminates this as a source of cross-contamination.
Reliable performance
Invitrogen Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, manufactured utilizing the SUS technology, is subjected to rigorous quality control testing (e.g., application-specific functional assays). Real-time PCR assays performed with Platinum Taq DNA polymerase manufactured using SUS technology demonstrates the same performance as compared to Platinum Taq DNA polymerase manufactured using conventional manufacturing scheme.

Figure 3. Sensitive, specific and reproducible amplification with DNA-free Taq DNA polymerase. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (red curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA.
Purity requirement
DNA-Free enzymes are analyzed following the highest standards to ensure the absence of nucleases and DNA contamination per the specifications described below (Table 1).
Table 1. Stringent quality testing to validate DNA-free Platinum Taq DNA polymerase.
| Purity test | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Exonucleases and endonucleases | undetected |
| RNases | undetected |
| Bacterial gDNA (16S rRNA) | ≤0.01 copy/enzyme unit |
| Human gDNA (Alu) | ≤0.001 copy/enzyme unit |
| Plasmid DNA (ori1) | ≤0.01 copy/enzyme unit |
Performance comparison of Platinum Taq DNA Polymerase, DNA-free versus competitors
Sensitivity
Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free helps enable accurate detection of low-copy (e.g., one copy) of target DNA. Uncompromised sensitivity is the advantage in PCR-based assays where the target DNA is in low concentration in the sample or when there is a limited amount of starting material (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Uncompromised sensitivity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, as compared to competitor. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Promega GoTaq MDx Hot Start Polymerase (green curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA.
Specificity
Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, offers the highest level of confidence in minimizing false positives from PCR based assays. False positives are signals generated in no template control (NTC) reaction in absence of template DNA. A highly specific test should not produce false positives or misclassify the identity of DNA target.

Figure 5. Uncompromised specificity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, as compared to competitor. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Promega GoTaq MDx Hot start Polymerase (green curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA. In 80 wells of negative control (no DNA template added), there was no E. coli DNA detected.

Figure 6. The purity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, helps ensure clean background in reagents-only/no-template controls (NTC). 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, or Promega GoTaq MDx Hot start Polymerase. PCR was run for 40 cycles with varying amount of E. coli gDNA (10–1,000 copies/reaction) or reactions with no added DNA.
Taq DNA polymerases purity
Many commercial providers of Taq DNA polymerase acknowledge the concern over DNA contamination and offer “DNA-free” enzymes for PCR based assays. These enzymes were compared to Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free. The results showed that Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, is the only enzyme with less than 1 copy of contaminating DNA in 100 units of enzyme (Table 2).
Table 2. Quality control standards for low-DNA contamination and DNA-free Taq DNA polymerases.
| Product | Copy No. of bacterial gDNA/100 Units | Copy No. of plasmid DNA/100 Units | Copy No. of human gDNA/100 Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.00 |
| Eurogentec HGS Diamond Taq polymerase | 11.7 | 300 | 0.04 |
| Roche Taq DNA polymerase, GMP grade | 18 | 80 | 0.12 |
| Roche AptaTaq DNA polymerase, LDx, glycerol-free | 4.1 | n.d. in 50 Units | 0.17 |
| Sigma MTP Taq DNA polymerase | 13.2 | 11,600 | 0.12 |
| Promega GoTaq MDx Hot Start Polymerase | 18.5 | 400 | 0.06 |
Sensitivity
Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free helps enable accurate detection of low-copy (e.g., one copy) of target DNA. Uncompromised sensitivity is the advantage in PCR-based assays where the target DNA is in low concentration in the sample or when there is a limited amount of starting material (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Uncompromised sensitivity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, as compared to competitor. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Promega GoTaq MDx Hot Start Polymerase (green curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA.
Specificity
Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, offers the highest level of confidence in minimizing false positives from PCR based assays. False positives are signals generated in no template control (NTC) reaction in absence of template DNA. A highly specific test should not produce false positives or misclassify the identity of DNA target.

Figure 5. Uncompromised specificity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, as compared to competitor. Performance of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free (blue curves), and Promega GoTaq MDx Hot start Polymerase (green curves) in qPCR assays were evaluated using primers targeting E. coli 16S rRNA gene and varying amount of E. coli input DNA. In 80 wells of negative control (no DNA template added), there was no E. coli DNA detected.

Figure 6. The purity of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, helps ensure clean background in reagents-only/no-template controls (NTC). 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, or Promega GoTaq MDx Hot start Polymerase. PCR was run for 40 cycles with varying amount of E. coli gDNA (10–1,000 copies/reaction) or reactions with no added DNA.
Taq DNA polymerases purity
Many commercial providers of Taq DNA polymerase acknowledge the concern over DNA contamination and offer “DNA-free” enzymes for PCR based assays. These enzymes were compared to Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free. The results showed that Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free, is the only enzyme with less than 1 copy of contaminating DNA in 100 units of enzyme (Table 2).
Table 2. Quality control standards for low-DNA contamination and DNA-free Taq DNA polymerases.
| Product | Copy No. of bacterial gDNA/100 Units | Copy No. of plasmid DNA/100 Units | Copy No. of human gDNA/100 Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-free | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.00 |
| Eurogentec HGS Diamond Taq polymerase | 11.7 | 300 | 0.04 |
| Roche Taq DNA polymerase, GMP grade | 18 | 80 | 0.12 |
| Roche AptaTaq DNA polymerase, LDx, glycerol-free | 4.1 | n.d. in 50 Units | 0.17 |
| Sigma MTP Taq DNA polymerase | 13.2 | 11,600 | 0.12 |
| Promega GoTaq MDx Hot Start Polymerase | 18.5 | 400 | 0.06 |
SUS manufacturing services–now available
Thermo Fisher Scientific offers a wide range of DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases with high quality and superior performance for your PCR- or qPCR-based assays. Now, we introduce Invitrogen Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-Free, manufactured utilizing a closed SUS-based technology. This will bring unparalleled confidence to your commercial scale, PCR-based assays. If you are interested in more information about Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, DNA-Free, or other DNA-Free enzymes, please contact us and we will work with you to meet your requirements.
References
Resources
OEM PCR, RT, qPCR enzymes & plastics
Additional PCR enzymes and reagents
Find variety of PCR enzymes and reagents for your applications, with the flexibility needed to perform your experiments.
Support
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.