Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Labeling and Detection Information

Learn about strategies and techniques for labeling proteins and antibodies for cell biology research. Topics include traditional reactive chemistries like amine and thiol labeling, protein-protein crosslinking, general protein crosslinkers and more. Newer chemistries for labeling proteins include click chemistry based protein and carbohydrate labeling reactions.
Labeling and detection features
On-demand webinar
A practical approach to antibody labeling
The growing number of fluorophores available makes labeling your own antibodies a tempting proposition, but with many antibody labeling solutions available, selecting the best option can be a daunting task.
Protein methods article

Overview of protein labeling
Labeling strategies result in the covalent attachment of different molecules, including biotin, reporter enzymes, fluorophores and radioactive isotopes, to the target protein or nucleotide sequence. While multiple types of labels are available, their varied uses are preferable for specific applications.
Labeling and detection subtopics
Labeling and detection learning resources
No records were found matching your criteria
| Type | Title | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Application note (2015) | Quantitation of proliferating cells with the EVOS FL Auto Imaging System | antibodies, antibody labeling, ArrayScan, cell proliferation, EVOS FL Auto Microscope, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, onstage incubator, phagocytosis |
| BioProbes articles (Issues 50–present day) | BioProbes Journal of Cell Biology Application | cell analysis, flow cytometry, imaging microscopy, immunoassays, antibodies, protein detection and quantification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Phycobiliproteins—Section 6.4 | antibody labeling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, multicolor flow cytometry |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Thiol-reactive probes excited with visible light—Section 2.2 | protein labeling, fluorescent dyes |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Thiol-reactive probes excited with ultraviolet light—Section 2.3 | protein labeling, fluorescent dyes |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Introduction to thiol modification and detection—Section 2.1 | antibody labeling, protein labeling, sulfhydryl modification, thiol labeling, thiol modification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Labeling small peptides with amine-reactive dyes in organic solvents—Note 9.2 | amine-reactive dyes, fluorescence, peptide labeling, protein modification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Derivatization reagents for carboxylic acids and carboxamides—Section 3.4 | amine-reactive dyes, amines, carboxylic acid modification, fluorescence, hydroxylamines, labeling chemistries, protein modification and crosslinking |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Click chemistry—Section 3.1 | azide and alkyne labeling reagents, azide–alkyne cycloaddition, bioorthogonal labeling, BrdU alternative, click reaction, Click-iT, EdU |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Reagents for analysis of low molecular weight amines—Section 1.8 | amine labeling, ATTO-TAG Reagents, dialdehydes: OPA and NDA, fluorescamine, protein modification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Kits for labeling proteins and nucleic acids—Section 1.2 | antibody labeling, nucleic acid labeling, protein labeling, protein modification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Introduction to amine modification—Section 1.1 | amine labeling, amine modification, antibody labeling, protein labeling, protein modification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Introduction to avidin–biotin and antibody–hapten techniques—Section 4.1 | antibodies, avidins and streptavidins, fluorescence, labeling and detection, secondary antibodies, secondary detection, signal amplification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Biotinylation and haptenylation reagents—Section 4.2 | antibody labeling, biotinylation, protein labeling, secondary detection, signal amplification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Biotin and desthiobiotin conjugates—Section 4.3 | antibody labeling, biotinylation, protein labeling, secondary detection, signal amplification |
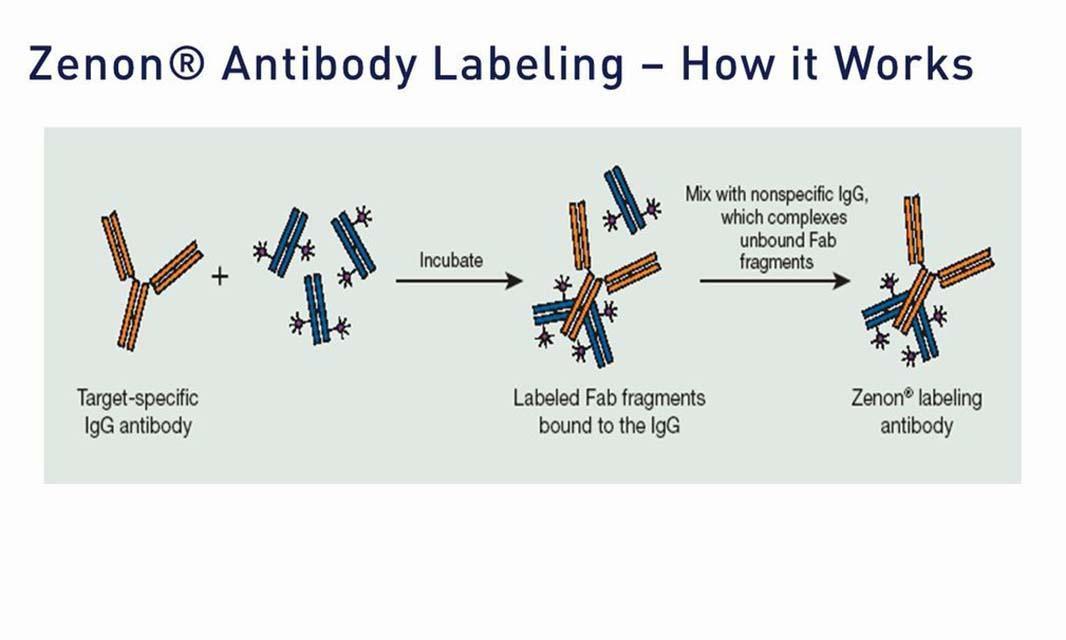
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Zenon Technology: Versatile reagents for immunolabeling—Section 7.3 | antibody labeling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, secondary detection, Zenon |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Introduction to antibodies, avidins and lectins—Section 7.1 | antibodies, avidins and streptavidins, fluorescence, labeling and detection, secondary antibodies, secondary detection, signal amplification |
| Molecular Probes Handbook | Avidin and streptavidin conjugates—Section 7.6 | antibodies, avidins and streptavidins, fluorescence, labeling and detection, secondary antibodies, secondary detection, signal amplification |
| Pierce Protein Methods | Overview of protein labeling | antibodies, antibody labeling, cell signaling, fluorescent dyes, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2007) | Evaluation of click chemistry-based alternative to BrdU antibody labeling in tissue and cultured cells using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry | antibodies, ArrayScan, cell cycle, cell proliferation, Click-iT, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, microplate reader, nucleic acid labeling |
| Scientific poster (2007) | Click catalyzed nucleic acid labeling as a novel replacement for BrdU antibody-based cell proliferation assay | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, antibody labeling, cell cycle, cell proliferation, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, nucleic acid labeling |
| Scientific poster (2008) | Zenon labeling technology facilitates detection of intra-cellular phosphoprotein determinants | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, cell signaling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescent dyes, protein labeling, rare cell detection, Zenon |
| Scientific poster (2008) | Detection of S-phase cell cycle progression using 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation with click chemistry | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, ArrayScan, cell cycle, Click-iT, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, microplate reader, nucleic acid labeling, nucleic acid quantitation |
| Scientific poster (2008) | ThiolTracker Violet dye, a new 405 nm excitable fluorescent probe for detecting intracellular thiols in imaging-based assays | ArrayScan, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, glutathione, high content analysis, microplate reader, protein labeling, violet laser-excited reagents |
| Scientific poster (2008) | Modified tumor cell protein expression and modification under physiological oxygen | Alexa Fluor, cancer, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, physiological oxygen level, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2008) | A new 405 nm excitable fluorescent probe of intracellular thiols for imaging and flow cytometric assays | ArrayScan, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, glutathione, high content analysis, microplate reader, thiol modification, violet laser-excited reagents |
| Scientific poster (2008) | Targeting serum glycoprotein cancer biomarkers with click chemistry | cancer, Click-iT, Electrophoresis gel, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2008) | Detection of DNA synthesis by automated microscopy and image analysis: Comparison of BRDU method and a new click chemistry-based EDU method | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, ArrayScan, cell cycle, cell proliferation, Click-iT, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, microplate reader, nucleic acid labeling |
| Scientific poster (2009) | Monitoring mitotic cells and DNA content by automated imaging and analysis | Alexa Fluor, cell cycle, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, nucleic acid labeling, nucleic acid quantitation, viability |
| Scientific poster (2009) | Click chemistry-based detection of nascent RNA synthesis using high content imaging and fluorescence microscopy | Alexa Fluor, ArrayScan, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, microplate reader, nucleic acid labeling, viability |
| Scientific poster (2009) | Non-radioactive targeting of multiple classes of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) with click chemistry | cell signaling, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein detection, protein enrichment, protein labeling, western blotting |
| Scientific poster (2009) | Quantitative analysis of genotoxicity and cytotoxicity to DNA damaging agents using high-content imaging | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, high content analysis, nucleic acid labeling, nucleic acid quantitation, viability |
| Scientific poster (2009) | Metabolic labeling and click chemistry detection of stem cell markers | Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein labeling, stem cell research |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Novel tools to enable high resolution gene expression by investigating the nascent transcriptome | Alexa Fluor, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gene expression, high content analysis, magnetic beads, nucleic acid labeling, PCR/qPCR, viability |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Click chemistry-based enrichment and identification of nascent and post-translationally modified proteins | cells, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein detection, protein enrichment, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Non-cytotoxic near-IR DNA stain for cell cycle analysis in living cells | cell cycle, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, fluorescent proteins, live-cell imaging, nucleic acid labeling, viability |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Click chemistry enrichment of cell surface glycoproteins | cells, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein detection, protein enrichment, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Identification and characterization of O-GlcNAc modification of galectin-1 in mesenchymal stem cells using click chemistry | Alexa Fluor, BacMam technology, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, immunocytochemistry (ICC), protein enrichment, protein labeling, western blotting |
| Scientific poster (2010) | Click chemistry-based universal enrichment columns for global identification of azide-modified proteins | Alexa Fluor, Click-iT, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein detection, protein enrichment, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2010) | A universal click chemistry-based enrichment column for the identification of multiple subclasses of PTM-modified proteins and newly synthesized proteins | Alexa Fluor, Click-iT, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, gel electrophoresis, protein detection, protein enrichment, protein labeling |
| Scientific poster (2011) | Site-specific click chemistry-mediated labeling of antibody glycans using metabolic and enzymatic approaches | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, antibody labeling, Click-iT, fluorescent dyes, western blotting |
| Tutorial | 3.2 Secondary antibody optimization–Fixed cell imaging: 5 steps for publication-quality images Secondary antibody detection protocols also need to be optimized for each primary antibody used. | antibody labeling, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), secondary antibodies, secondary antibody protocol, secondary detection |
| Tutorial | 2.2 Primary antibody protocol optimization–Fixed cell imaging: 5 steps for publication-quality images Every primary antibody must be optimized separately. There are many protocols available, and it is important to understand a "one size fits all" approach gives inferior results, as every antibody is slightly different. Learn how to approach optimization. | antibody labeling, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), primary antibodies, primary antibody protocol |
| Tutorial | 3.5 Dye choice and special concerns–Fixed cell imaging: 5 steps for publication-quality images There are many different dyes spanning the visible, far-red, and infrared wavelengths.Considerations for making the right choices for your experiment are presented. | dye choice, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, Fluorescence SpectraViewer, immunofluorescence (IF), label choice, multiparametric dye selection |
| Tutorial | 2.1 Primary antibody choice–Fixed cell imaging: 5 steps for publication-quality images After preparation, the second step to publishable images is to label the sample, usually involving primary antibodies to your specific targets of interest. The antibody source, the use of direct versus labeled antibodies as well as the validation for specific applications is discussed. | antibody labeling, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), primary antibodies |
| Tutorial | 3.1 Secondary antibody choice–Fixed cell imaging: 5 steps for publication-quality images Step three of the five steps in making publishable images is to detect the label. That is, to detect with a secondary antibody, for instance, or an amplification technique, as well as to determine what controls to use. Your options are discussed. | antibody labeling, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), secondary antibodies, secondary antibody, secondary detection |
| Tutorial | Labeling a purified antibody Educational video on how to label your next antibody for imaging or fluorescence. Walk through the tutorial as Molecular Probes scientists demonstrate the protocol—including all the tips and tricks you'll want to know about for your next antibody labeling experiment. The video features Judie showing Curtis, a chemistry graduate student, how to label his monoclonal antibodies while saving time and maximizing yield. | antibodies, antibody labeling, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, immunofluorescence (IF) |
| Video | How to site specifically label your antibody using SiteClick technology This video explains how to easily and site specifically label an antibody using an enzymatic and Click chemistry approach. This method can be applied to any intact IgG antibody and requires no antibody engineering or complex methodology. Unlike classic antibody conjugation techniques this breakthrough SiteClick technology allows for antibody conjugation with complete confidence that the label will not directly interfere with the antibody binding domain. | antibodies, antibody labeling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, Qdot, western detection |
| Webinar | Fixed cell imaging—Five steps for publication-quality images With over 40 years dedicated to cell imaging research, we offer long-proven tools and protocols to help confidently create quality cell images the first time. This on demand webinar covers the 5 essential steps to getting great images. | antibodies, blocking, Celleste, dyes, EVOS FL Auto 2.0, fixation, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF), sample detection, sample labeling, sample preparation, signal amplification |
| Webinar | Learn to choose the right fluorophore when designing experiments The choice of fluorophore is one of the first important decisions to make in developing an experiment. Fluorophores are compounds that emit light at a specific wavelength when they have been excited at another, lower wavelength. Join our webinar and explore: How to choose the best organic dye for an assay Quantum dots and how they compare to other dyes When to use a phycobiliprotein like R-PE or APC When to use fluorescent proteins like GFP How to choose a suitable dye to match your instrument In addition, we will explore the basic characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of the various fluorophores to help you choose and develop the best assay for your needs. | antibodies, antibody labeling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, fluorescent dyes, fluorescent proteins |
| Webinar | A practical approach to antibody labeling The growing number of fluorophores available makes labeling your own antibodies a tempting proposition. But with many antibody labeling solutions available, selecting the best option can be a daunting task. In this webinar we will: Provide an overview of our antibody labeling kits Offer guidance on which methods are ideal for specific applications and experiments Provide tips and tricks to optimize your labeling protocol | antibodies, antibody labeling, flow cytometer/flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF) |
| Webinar | An introduction to immunofluorescence staining of cultured cells In this webinar, we discuss the steps of an immunofluorescent staining protocol including material list, common variations, and necessary controls. We'll also provide a simple troubleshooting guide and examine how to avoid common pitfalls. Presented by Jason Kilgore, Technical Support Specialist, Thermo Fisher Scientific. | antibodies, antibody labeling,antifades, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunofluorescence (IF) |
| Webinar | A comparison of basic immunofluorescent labeling strategies In this free webinar, we will compare different immunofluorescent labeling strategies exploring the pros and cons of each method. You will learn when the use of a direct conjugate is appropriate and when amplification techniques can be utilized. We'll also present a simple decision tree to aid in determining the best method for each situation. | Alexa Fluor, antibodies, antibody labeling, fixed-cell imaging, fluorescence microscopy/fluorescence imaging, immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunofluorescence (IF) |
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.