Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
The Wittig Reaction is a chemical reaction that converts aldehydes or ketones into alkenes
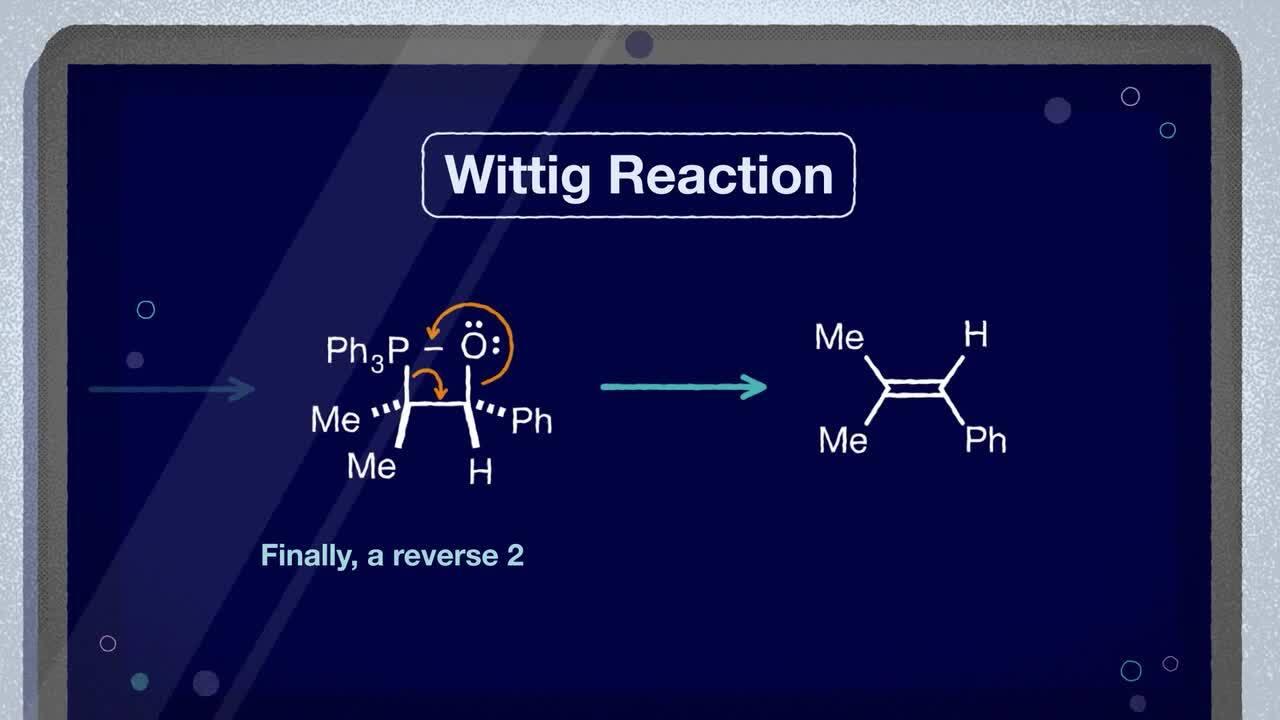
The Wittig Reaction is the chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide (the Wittig reagent) to afford an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide.
History of the Wittig Reaction
In the early 1950s, chemists Georg Wittig and Georg Geissler reported the reaction of methylenetriphenylphosphorane and benzophenone to form 1,1-diphenylethene and triphenylphosphine oxide in quantitative yield. Wittig recognized the importance of this reaction and carried out a comprehensive series of experiments in which several phosphoranes were reacted with various aldehydes and ketones to obtain the corresponding olefins. The reaction between carbonyl compounds and phosphoranes to generate carbon–carbon double bonds has subsequently become known as the Wittig reaction. Since its discovery, the Wittig reaction has become one of the most widely used synthetic techniques for the formation of alkenes.
The Wittig reaction has several important variants. One of the most notable is the Horner–Wittig reaction, which occurs when the phosphorus ylides are based on phosphine oxides rather than triarylphosphines. When stabilized alkyl phosphonate carbanions are used to create (E)-alpha, beta-unsaturated esters, the reaction is known as the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction. Another variant, the Schlosser modification, generates pure E-alkenes when two equivalents of a lithium halide salt is present during the ylide addition step.
The total synthesis of the alkaloid natural product buflavin utilized the Horner–Wittig reaction between a biaryl aldehyde and a metalated carbamate.
Other Carbonyl Compound Reactions
Other Carbonyl Compound Reactions include:
-
Grignard Reaction -
Knoevenagel Condensation -
Mannich Reaction -
Reformatsky Reaction
For other types of reactions, visit our Named Reactions page.
Acroseal Packaging
Chemical reactions often involve the use of air- and moisture-sensitive solvents, and pyrophoric or hazardous reagents. Our AcroSeal packaging is a packaging solution designed to enable safe handling of these types of materials which are used in a variety of research and development applications, including NMR analysis and studies in drug discovery, agrochemicals, flavors and fragrances, and more.
Watch our video for more information.